All about the House Mouse Biology Diagrams Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) In the food chain 'grass --> grasshopper --> frog --> snake --> eagle', what organism is the primary consumer?, 1) In the food chain 'grass --> grasshopper --> frog --> snake --> eagle', what organism is the producer?, Which of the following links of the food chain eats decaying matter? and more. The following shows 3 different food chains. In the first one corn is our producer, which is eaten by a mouse (the primary consumer), and the mouse is eaten by the owl (the secondary consumer). The second food chain is little longer, therefore showing the tertiary consumer, which is the lion in this example. Few mammals are lower on the food chain or closer to the outside of the food web than the mouse. Just about every other carnivorous or omnivorous animal will gladly eat a mouse when given the chance. As for the question of what do mice eat?: In the wild, they eat a variety of seeds, vegetation and insects. What Eats Mice? Gordon Ramel April
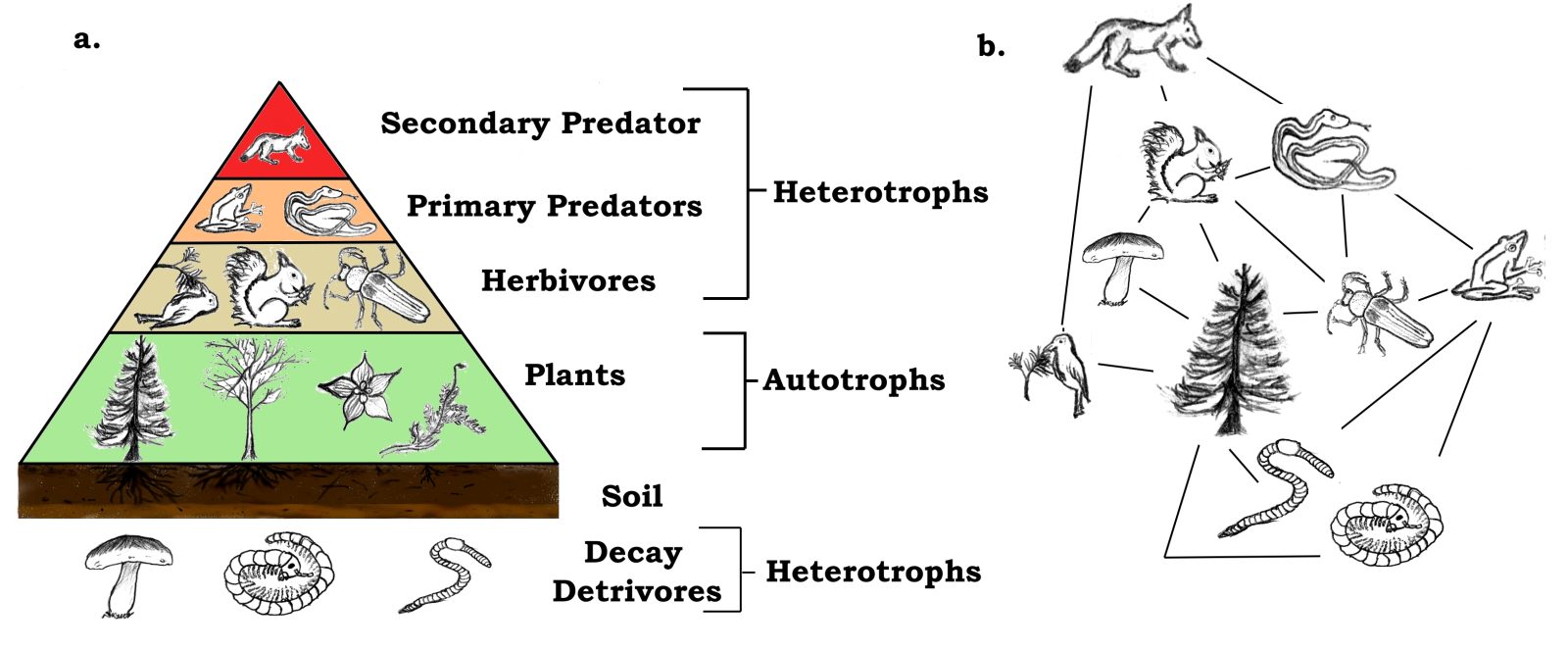
What many people don't realize is that mice are a keystone species in virtually every terrestrial ecosystem in the world. 1 Take a look at this food-chain pyramid It illustrates from plants upward each animal group that's prey for the levels above it. Plants, at the bottom, are food for herbivores and they, in turn, are food for omnivores The humble house mouse, a common sight in homes and fields across the globe, is a vital part of the food chain. They are consumed by a wide variety of predators. These include cats, foxes, weasels, ferrets, mongooses, large lizards, snakes, hawks, falcons, and owls .

Definition, Trophic Levels, Types, and Example Biology Diagrams
A food chain shows a single feeding pattern between a predator and a prey in an ecosystem. However, in reality, the relationship between them is much more complex. An organism can have multiple food sources (prey) and simultaneously be eaten by multiple predators. Such a relationship is represented pictorially using a food web. Deer mice play significant roles within the ecosystems they inhabit, impacting both the food chain and the surrounding plant life. Contribution to the Food Chain. As omnivores, deer mice occupy an intermediate position in the food chain. They act as both consumers, feeding on plants and insects, and prey for various predators. The North American field mouse has a similar diet to that of other species of mice. It is omnivorous , which means that it eats both plant and animal matter. Field mice commonly prey on arthropods, and caterpillars are one of their favorite meals. Their primary plant food source is seeds, though they also eat nuts, flowers, fruits, and fungi.
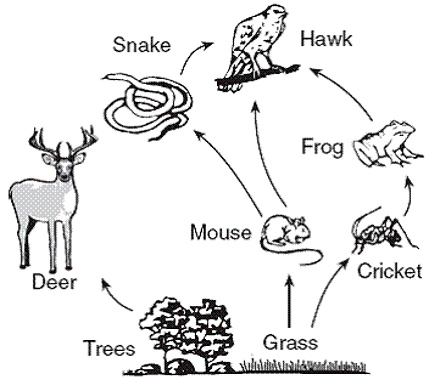
Mice play an important part in the local food chain. Although most species of mice are omnivores, meaning that they eat insects, fruits, seeds and vegetables, they also provide food for larger animals, including: but in the wild, many mice create tunnels or ground burrows to create their living spaces. During their digging and burrowing The diet of a pet mouse differs only slightly from that of a wild mouse. They are still typically the predator of a mouse depends on the habitat. In general, mice tend to be pretty low on the food chain. The most common predators of the genus Mus include owls, hawks, skunks, and snakes. Owls are exceptional hunters when it comes to finding
