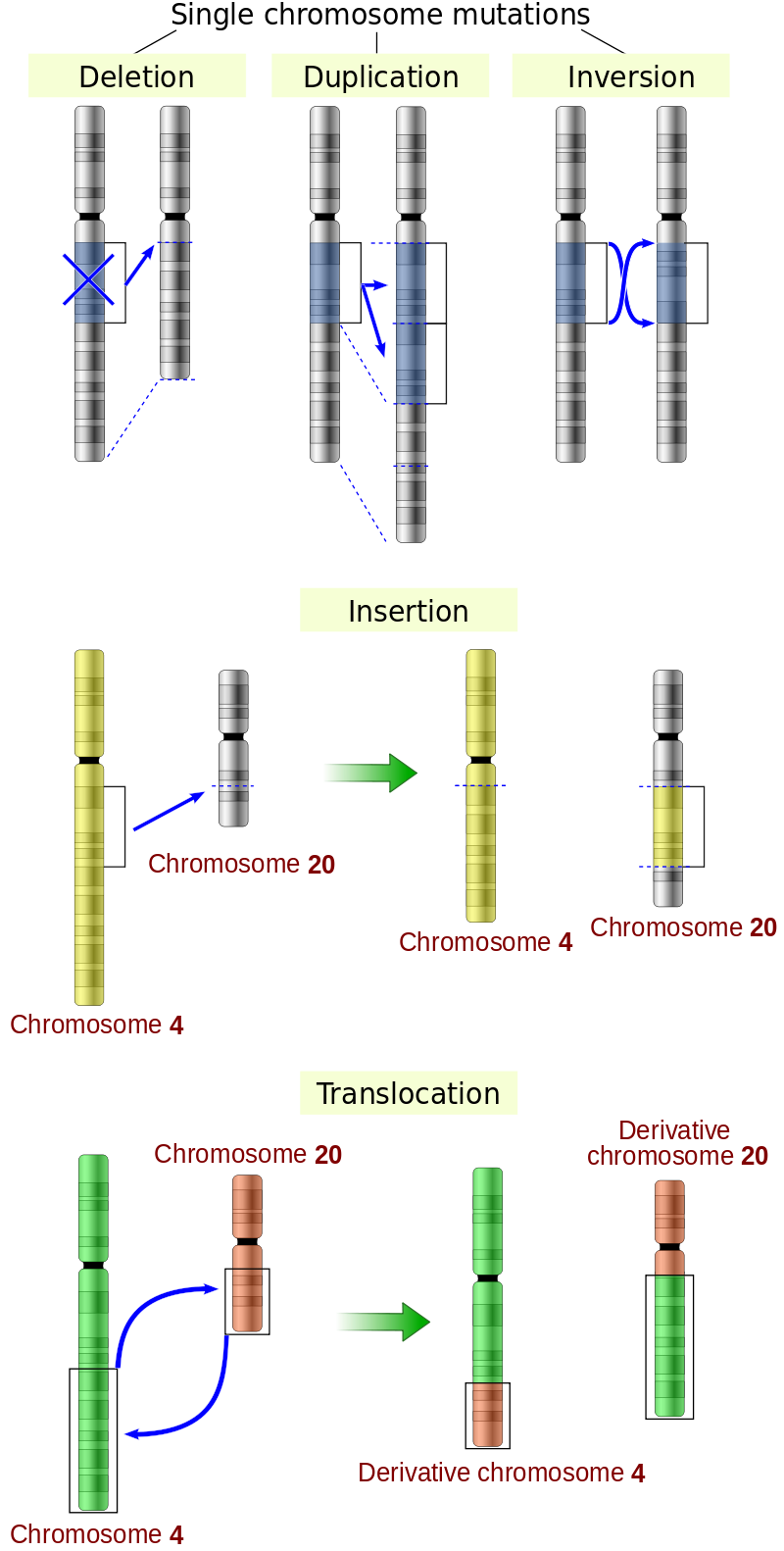
BOFELSEFE MUTASYON Biology Diagrams An example of an insertion mutation. Deletion of nucleotides A mutation that occurs when a nucleotide (and therefore its base) is randomly deleted from the DNA sequence is known as a deletion mutation. Like an insertion mutation, a deletion mutation changes the amino acid that would have been coded for. Like an insertion mutation, a deletion mutation also has a knock-on effect by changing the Errors and Mutations in Division. While cell division is a highly regulated process, errors can occur, leading to mutations with significant biological consequences. Mistakes during mitosis, such as nondisjunction or chromosome misalignment, can result in aneuploidy, a condition where cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes. The ability to reproduce is one trait that sets living organisms apart from nonliving matter. The flow of life is based on cell division or the reproduction of cells. Cell division can play a different role in different organisms. For example, when a prokaryotic cell generally divides, it has completely reproduced because it gives rise to a new organism. However, in multicellular eukaryotes
In humans, a rare genetic disease called Mosaic Variegated Aneuploidy stems from mutations in the BUB1B gene, and afflicted individuals show a very high proportion of aneuploid tissue cells. These patients suffer from a variety of serious pathologies, including growth defects, microcephaly, and increased cancer incidence [ 76 , 77 , 78 ].

Linking abnormal mitosis to the acquisition of DNA damage Biology Diagrams
This occurs via two distinct, but not mutually exclusive, mechanisms: the acquisition of genetic mutations, and gene copy number changes. Genetic mutations arise as a consequence of cells failing to efficiently detect Prolonged mitosis gives rise to DNA damage through multiple mechanisms. Prolonged mitosis leads to depletion of many Mitosis and Cancer. DNA, sometimes called a genetic blueprint, contains the hereditary material in nearly all organisms. The improper copying of DNA produces two types of errors, or mutations. Silent mutations have no impact on the DNA sequence, but missense mutations, which alter amino acid sequences, often impact the associated function. For example, there are genetic variations that arise in clonal species, such as bacteria, due to spontaneous mutations during mitotic division. Furthermore, chromosomes are sometimes replicated

Genetic mutations are changes to your DNA sequence. Genetic mutations could lead to genetic conditions. During mitosis, your genes instruct your cells to split into two by making a copy of your chromosomes. Meiosis: The process of making egg and sperm cells for the next generation. During meiosis, chromosomes copy themselves with half the When Do Gene Mutations Occur? Mutations frequently occur just before the process of mitosis when DNA is being replicated in the cell nucleus. During mitosis or meiosis, mishaps can occur when chromosomes are not lined up correctly or fail to separate properly.Chromosomal mutations in the germ cells can be inherited and passed along to the next generation. In mitosis, genetic recombination can occur, leading to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process, known as crossing over, is an important mechanism for genetic variation and evolution. Genomic instability refers to the increased rate of DNA mutations and chromosomal rearrangements in cancer cells. It can
