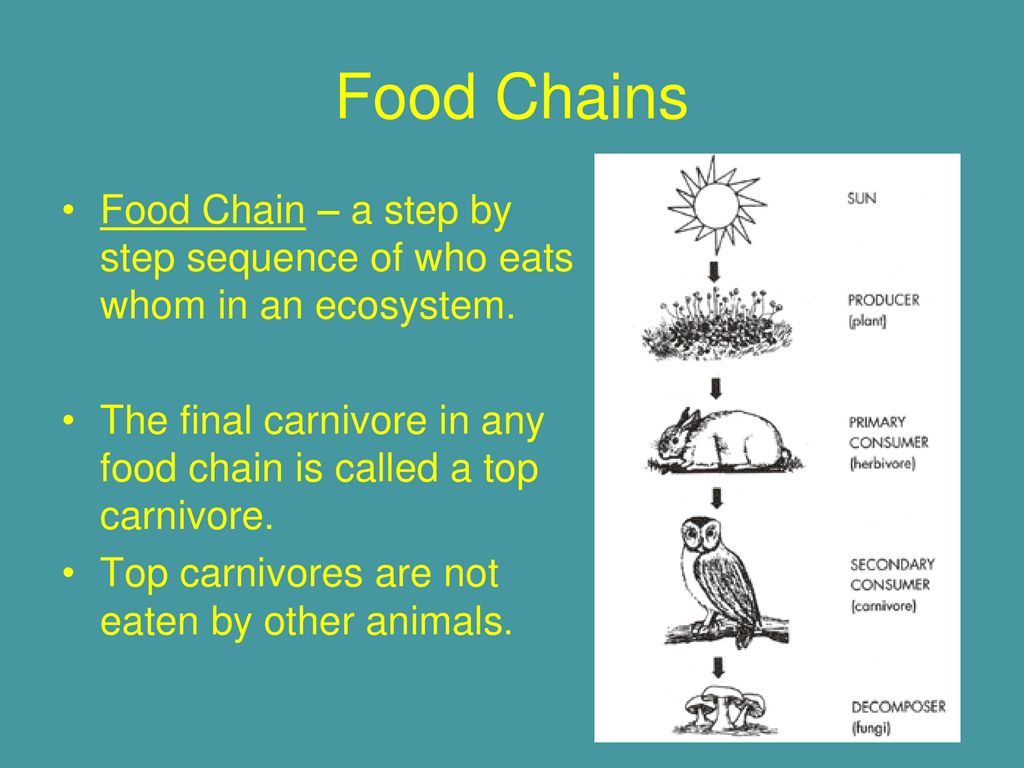
Carnivore food chain Biology Diagrams A food chain describes how living organisms get their food. All organisms, from the most complex to the most simple ones, need food to survive. Living things can be part of multiple food chains and all connected food chains in an ecosystem combine to make a food web.. As shown in the infographic below, a basic food chain is composed of producers, consumers, and decomposers. A trophic level represents an organism's position in a food chain, indicating how it obtains energy. Food chains always begin with producers (like plants) that create their own food through photosynthesis. Next come primary consumers (herbivores) that eat the producers. Secondary consumers (carnivores or omnivores) then eat the primary Different Types of Food Chains: Types: Description: Grazing Food Chain: Energy flow starts with green plants, which are consumed by herbivores, followed by carnivores. Common in terrestrial ecosystems. Detritus Food Chain: Energy flow begins with dead organic matter broken down by decomposers, then consumed by detritivores. Common in
It's important to distinguish between a food chain and a food web. A food chain is a simplified linear representation of energy flow through an ecosystem (e.g., plant → herbivore → carnivore). A food web, on the other hand, is a much more complex and accurate model showing the interconnectedness of numerous food chains. Most animals are Definition: Carnivores are organisms that obtain their energy and nutrients by consuming other animals. They are often referred to as secondary or tertiary consumers in a food chain. Role in the Food Chain: Carnivores occupy different levels in the food chain depending on their feeding habits. Role of carnivores in food chains. Carnivores play a crucial role in food chains. They help to control the population of herbivores. If the number of herbivores is not controlled, they will eat all the plants, and this will lead to the destruction of the ecosystem. Carnivores also help to maintain the balance in the food chain.

Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples, and Diagram Biology Diagrams
The top predator of a food chain is the carnivore within the community that does not have any predators of its own. When the top predator dies, their remains are broken down by decomposers—bacteria and fungi. Decomposers return nutrients back to soil to help restart the food chain.An example of a marine food chain starts with seaweed as the Each food chain consists of several trophic levels, which describe an organism's role in an ecosystem. Carnivores and omnivores occupy the third trophic level. An omnivore, such as a human, is an organism that eats plants and animals. Many carnivores get their energy and nutrients by eating herbivores, omnivores, and other carnivores. The These carnivores may eat insects and worms. Carnivorous animals have strong jaws and sharp teeth to enable them to tear and rip prey. These animals often have long, sharp claws that they also use to tear prey. Carnivores depend on sufficient prey in the food chain to give them the food they need.