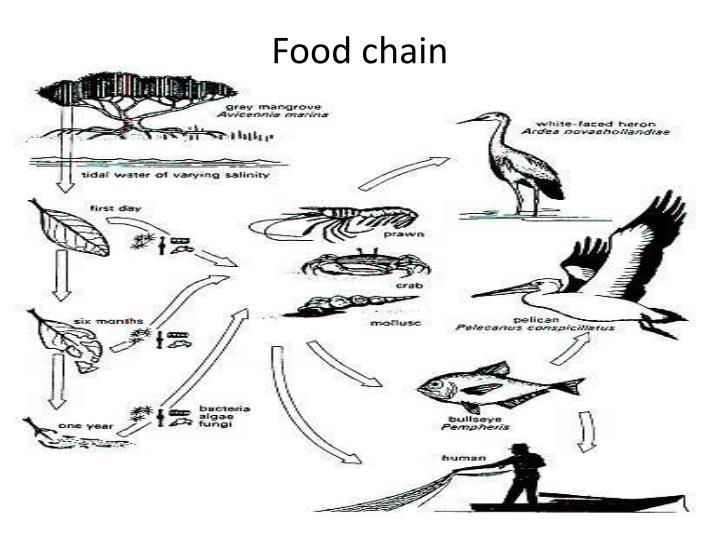
Could be basis for new Diagram MangroveFoodWeb Biology Diagrams These food chains are interconnected, which leads to the formation of complex food webs that tell us about the relationship between multiple organisms and their interactions. Food chains are categorized based on the role of organisms in the ecosystem and are named: Detritus Food Chain, Grazing Food Chain, and Parasitics Food Chain.

They have an incredible amount of biodiversity, illustrated in swamp food chains and swamp food webs. A food chain is a linear diagram of the feeding relationships between organisms in an • Swamp food chain magnets • Saltmarsh food chain magnets • Food chain arrows and labels (energy, producer, consumer, decomposer) • Trash (water bottle, fork, straw, plastic bag) Background A food chain is a series of organisms that show the transfer of energy from one to the next. Most food chains on earth get their energy from the sun. Unlike a simple food chain, which follows a single path, a food web shows an ecosystem's many overlapping food chains. This helps us understand how energy flows from one organism to another and how they all depend on each other to survive. In the Everglades, the food web includes plants, herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, decomposers, and
Food Web: Concept and Applications Biology Diagrams
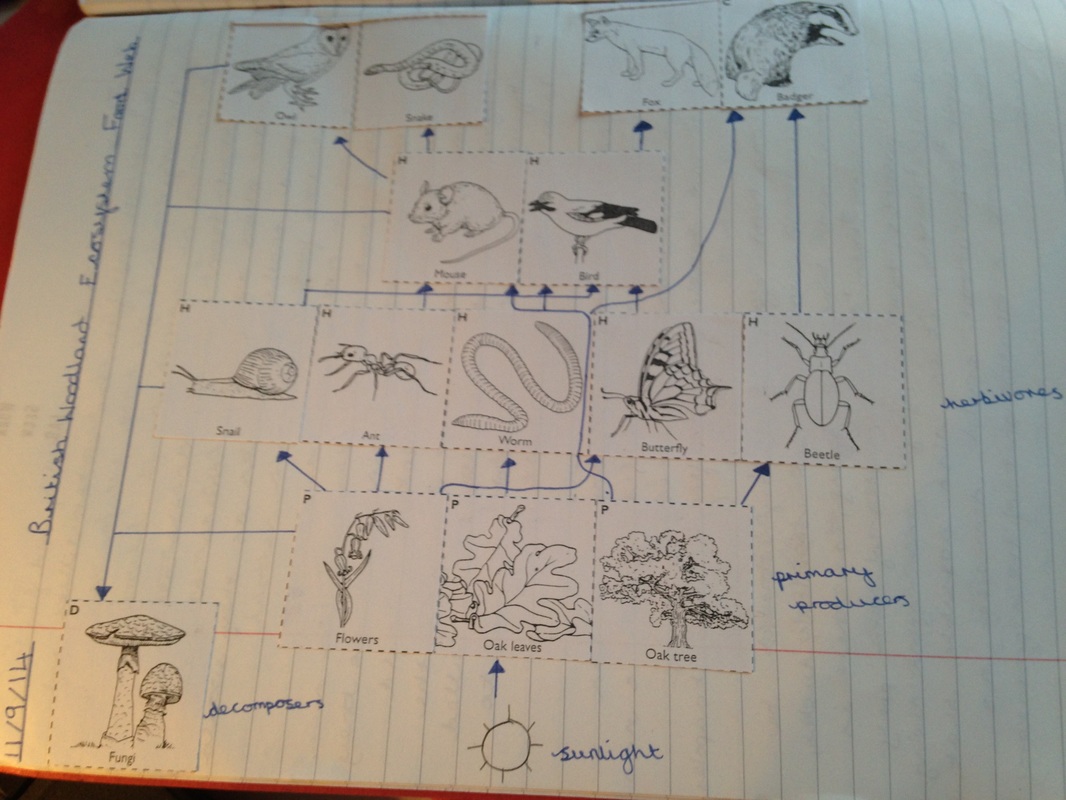
Food web interactions. Although depictions of food webs often show direct single-line paths of consumption from producers to consumers on various trophic levels like food chains do, they can also show the ways in which some organisms diverge from these patterns. For example, larger carnivores and omnivores whose diets are not limited to a few types of animals may also eat primary consumers if

The components of the chain may also shift in the absence or presence of new plants, animals, and physical conditions. Read more. A great example to illustrate how a swamp's food chain has a cyclical nature is the natural death of a crocodile. In the wild, an adult crocodile's large carcass may become a source of energy for multiple levels Wetland food webs are the complex relationships between the organisms that live in wetland ecosystems. At the base of the food web are the producers - the aquatic plants like cattails, lily pads, and reeds that use sunlight to produce their own food through photosynthesis. These plants provide food and habitat for a variety of consumers.
Definition, Ecosystem, Food Chain, & Examples Biology Diagrams
Food webs are part of an ecosystem, and can be used to simplify and understand the connections between different kinds of organisms, including their behavior and interactions. A food web visually maps out the interconnections between producers and consumers, containing all the food chains of an ecosystem. The Cyclical Nature of the Food Chain A cyclical food chain means that even the most fearsome creatures can become a source of nutrients to lower-order consumers and decomposers. Rawpixel Ltd / CC BY 2.0. In any type of ecosystem, a "food chain" can be defined as a series of organisms depicting the transfer of energy (in the form of
