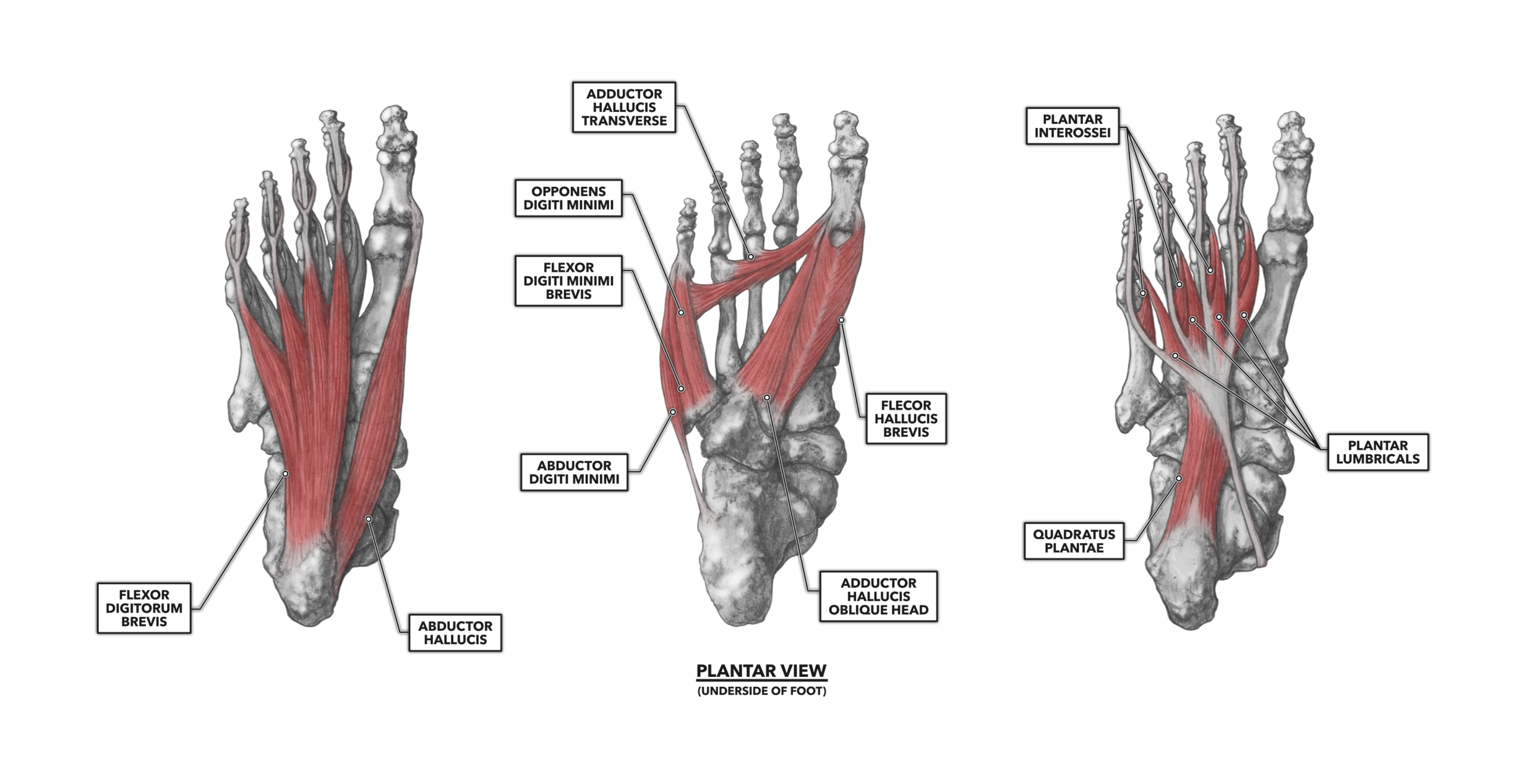
Detailed Foot Muscles Human Anatomy for Medical Education Biology Diagrams The extrinsic muscles of the foot originate in the lower leg, whilst the intrinsic muscles are contained within the foot itself. The intrinsic foot muscles act to stabilise the foot and support the arches, as well as to produce fine movement of the toes. The intrinsic foot muscles can be divided into two main groups, plantar and dorsal. Learn about the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the foot, their origins, insertions, actions, and nerve supply. The web page covers the dorsal and plantar aspects of the foot, with diagrams and descriptions of each muscle.

The muscles of the dorsum of the foot are a group of two muscles, which together represent the dorsal foot musculature. They are named extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis. The muscles lie within a flat fascia on the dorsum of the foot (fascia dorsalis pedis) and are innervated by the deep fibular or peroneal nerve. There are 29 muscles associated with the human foot: 10 originate outside the foot but cross the ankle joint to act on the foot, and 19 are intrinsic foot muscles. The foot is crucial to human locomotion and postural stability, and the muscles associated with the foot are therefore involved principally in this function. The muscles are aided by the plantar fascia, shaping the posture, shape
The Muscles of the Leg and Foot: 3D Anatomy Model Biology Diagrams
Learn about the anatomy and function of the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the foot. See 3D models, diagrams and quizzes of the dorsal and plantar aspects of the foot muscles. Learn about the complex structure and function of the human foot, which contains 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 moving parts. Find out how the foot supports your weight, allows for locomotion, and can be affected by various injuries and disorders.

These muscles contract to plantar flex the foot --- such as when standing on your tiptoes --- and flex the toes. Shin muscles, such as the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus, dorsiflex the foot and extend the toes. The muscles of the calf also work subtly to stabilize the ankle joint and foot and to maintain the body's balance. Learn about the anatomy of the ankle and foot, including the bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles. Find out how the foot differs from the hand and how it supports body weight and movement.
