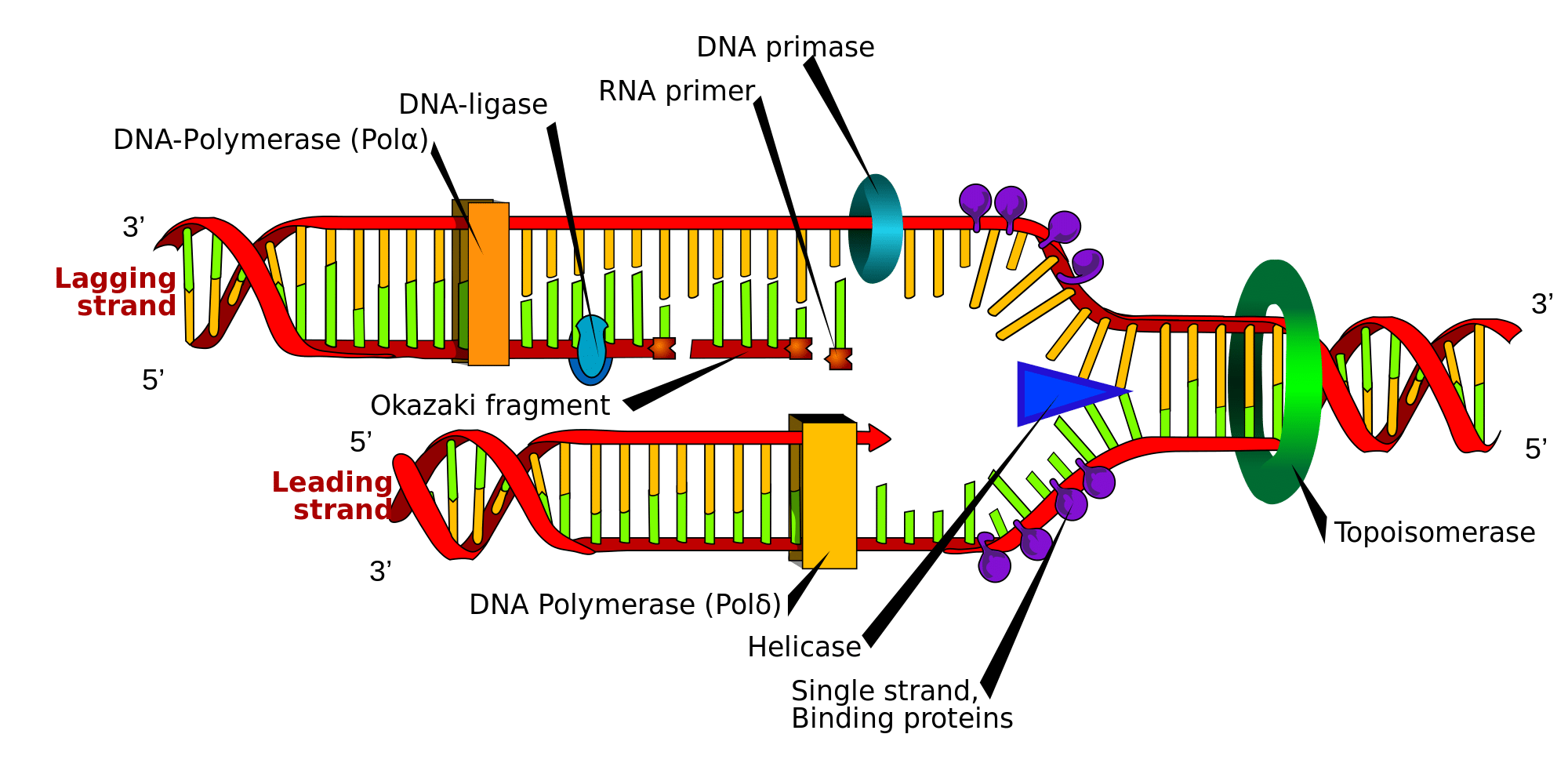
DNA replication of prokaryotes Biology Diagrams DNA replication's primary purpose is to enable living organisms to reproduce. The only way to replace the cells is to copy the cell's information. It happens in the S phase of cell division. DNA must replicate before cells divide so that the two resulting daughter cells contain the same genetic information as the parent cell. The most important event occurring in S phase is the replication of DNA. The aim of this process is to produce double the amount of DNA, providing the basis for the chromosome sets of the daughter cells. DNA replication begins at a point where regulatory pre-replication complexes are attached to the DNA in the { G }_{ 1 } phase. These complexes S Phase. S phase is the period of wholesale DNA synthesis during which the cell replicates its genetic content; a normal diploid somatic cell with a 2N complement of DNA at the beginning of S phase acquires a 4N complement of DNA at its end. (Recall that N = 1 copy of each chromosome per cell [haploid]; 2N = 2 copies [diploid].) The duration of S phase may vary from only a few minutes in
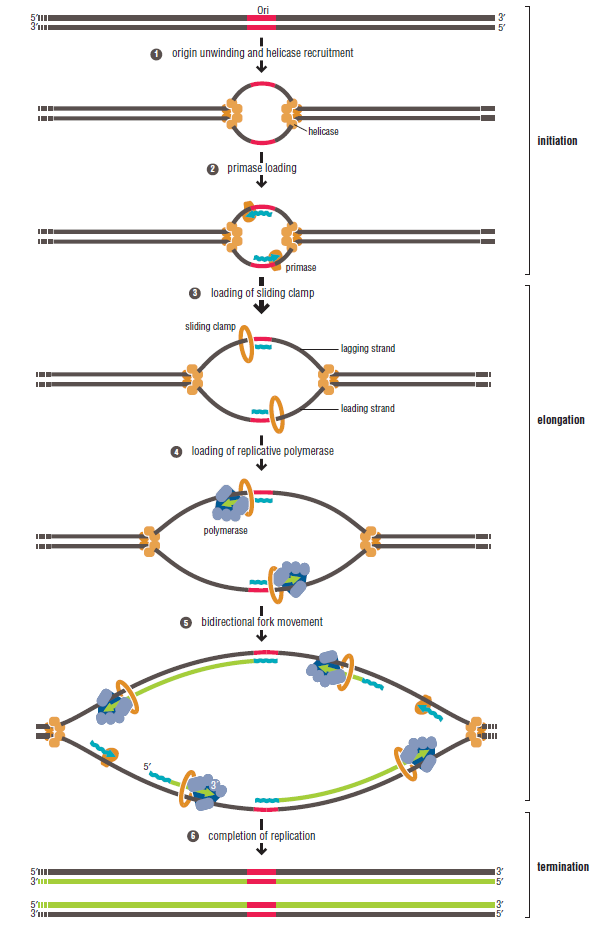
Initiation and completion of DNA replication defines the beginning and ending of S phase of the cell cycle. Successful progression through S phase requires that replication be properly regulated
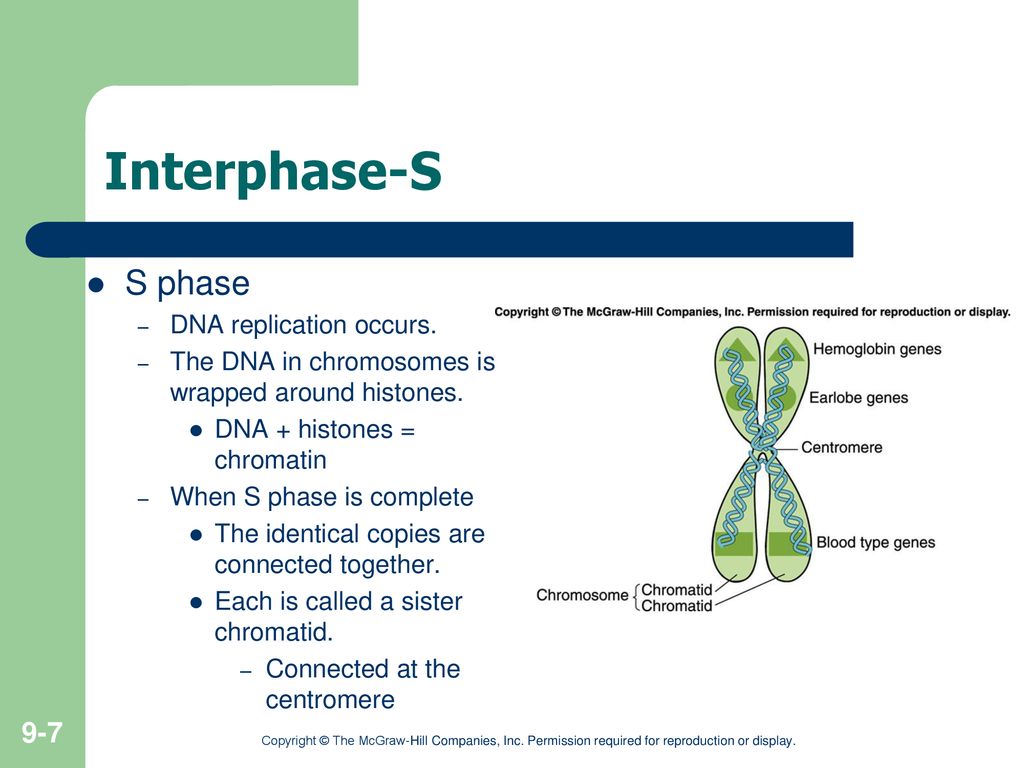
Phase: Explanation and Review Biology Diagrams
The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase, or S phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. The elucidation of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how DNA is copied.
The somatic eukaryotic cell cycle is a series of phases: G1, S, G2, and mitosis. Cells start the cell cycle in G1 (gap phase 1) progress through S (DNA replication), G2 (gap phase 2), and then divide in M (mitosis) . Cells enter G1 either from the preceding mitosis and cytokinesis or from a quiescent state (also known as G0 phase) which is S phase DNA replication is a crucial process in the cell cycle where DNA is duplicated, preparing the cell for division. It involves the unwinding of the DNA double helix, the synthesis of new DNA strands complementary to the existing ones, and the formation of new DNA molecules. Two main structures, the helicase enzyme and the replication fork, play key roles in this process.
+happens+during+the+S+phase+of+the+cell+cycle+and+not+during+mitosis.jpg)
9.2: DNA Replication Biology Diagrams
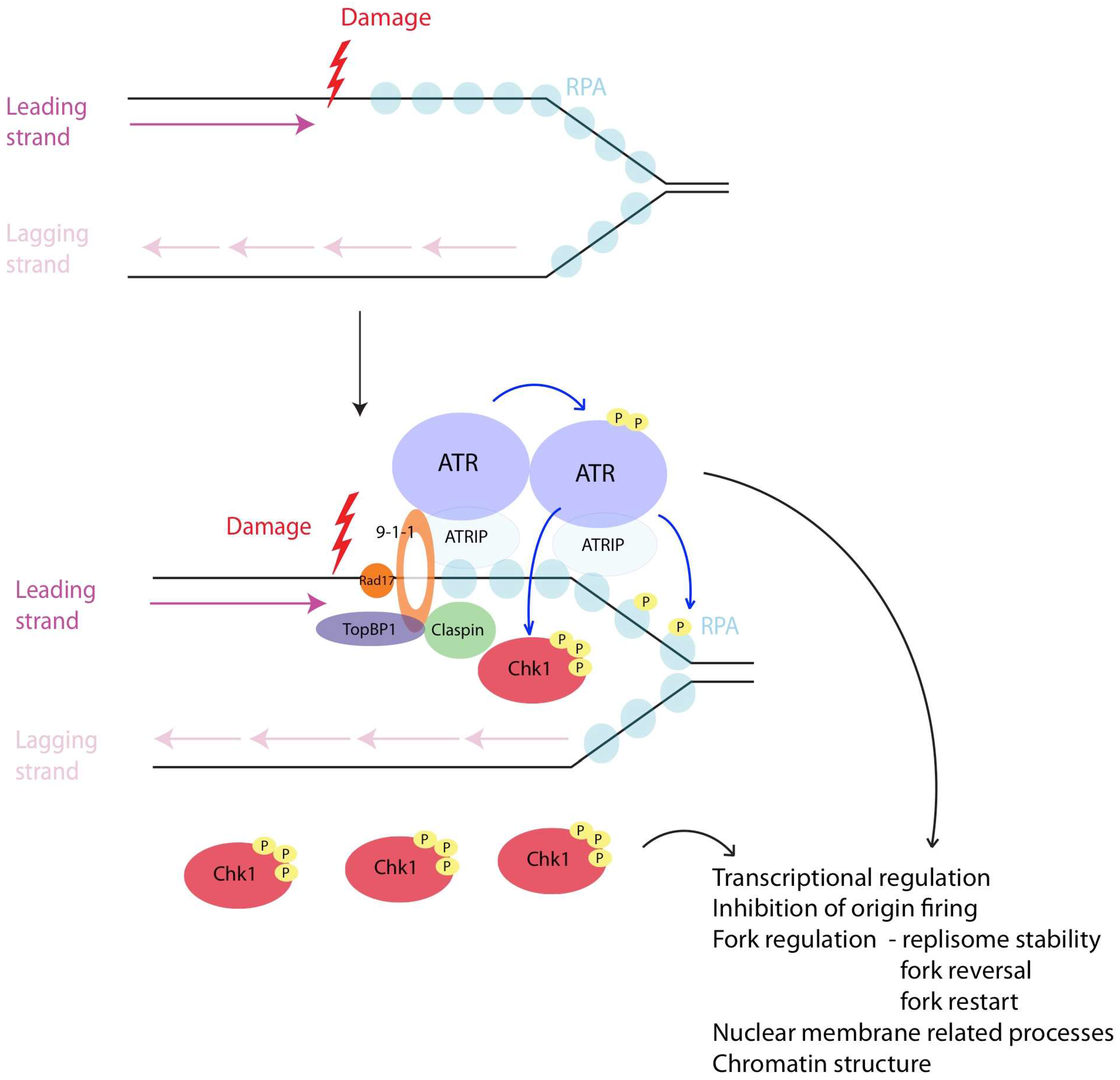
During S-phase, the cell converts pre-RCs into active replication forks to initiate DNA replication. [4] This process depends on the kinase activity of Cdc7 and various S-phase CDKs, both of which are upregulated upon S-phase entry. [4] Activation of the pre-RC is a closely regulated and highly sequential process. During S phase, any problems with DNA replication trigger a '' checkpoint" — a cascade of signaling events that puts the phase on hold until the problem is resolved. The S phase checkpoint CHAPTER 42 S Phase and DNA Replication. Accurate replication of DNA, which is crucial for cellular propagation and survival, occurs during the S phase (DNA synthesis phase) of the cell cycle.This chapter begins with a brief primer on the events of replication and then discusses its regulation. Next, the chapter covers the proteins that bind origins of replication and ensure that each region of