forest food chain Recherche Google Biology Diagrams Food Webs A food chain shows how an animal gets energy from one food source. But food chains can overlap. One kind of producer may be food for different kinds of consumers. Some consumers may eat different kinds of food. When two or more food chains overlap, they form a food web. In a food web, at least one plant or animal from each food chain Woodpeckers' favorite foods: Insects Grubs, spiders, ants, mealworms, and wood-boring bugs. Fun fact: half of a Pileated Woodpecker's warm-weather diet may be comprised of ants. Tree sap. This sweet treat often sustains the species in the spring when few other foods are available. Nuts. Peanuts and peanut butter are favorite finds for

The woodpecker family, Picidae, fills a unique niche in the food-gathering chain. Woodpeckers drill into trees to uncover insect food, to create nesting shelters and to communicate with other woodpeckers. A number of body adaptations make this drilling possible. A woodpecker has a sharp, stout bill with a chisel-like tip for
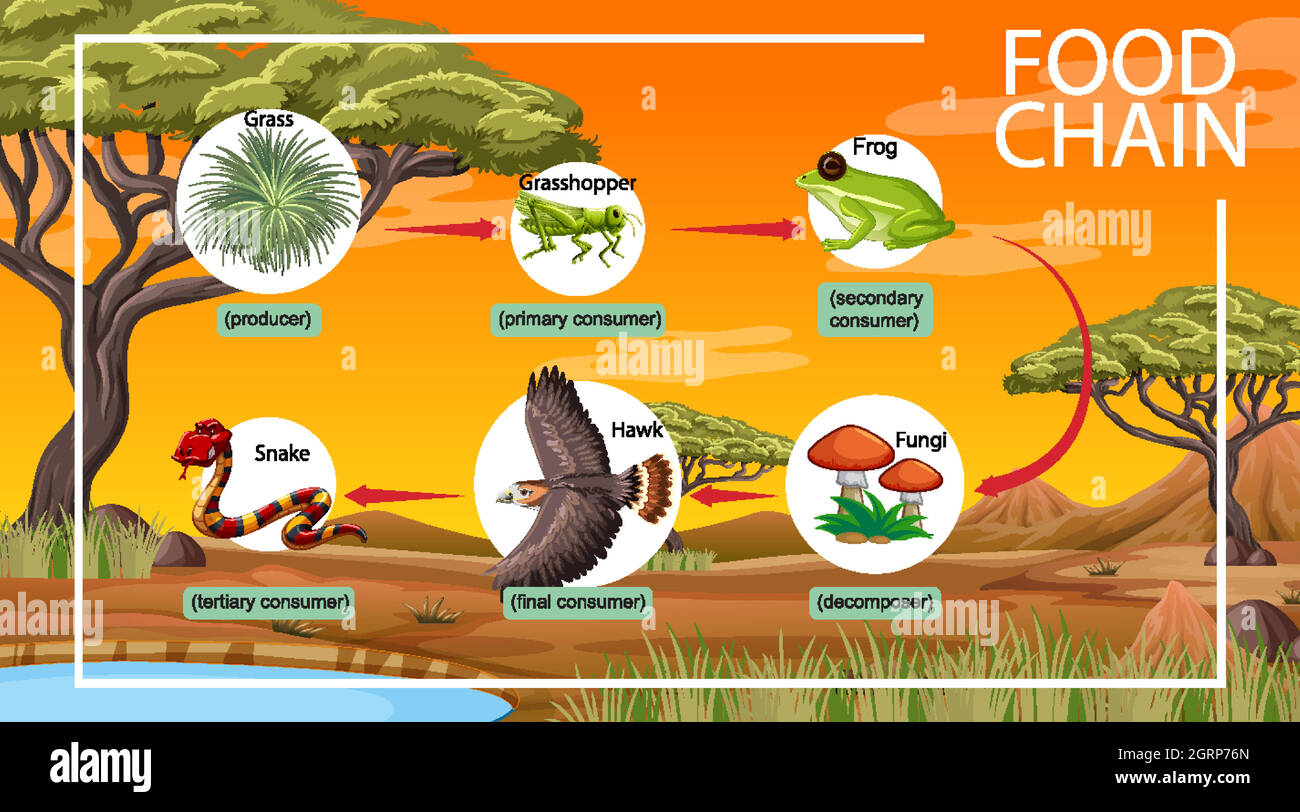
Food Chains In A Woodland Habitat Biology Diagrams
Acorns are a preferred food for various birds, including woodpeckers, jays, and pigeons, as well as mammals such as squirrels, deer, and wild boars. The primary food chain in a forest ecosystem consists of producers such as plants that use photosynthesis to create their own food, primary consumers such as herbivores that eat the producers
Coniferous Forest Food Chain. Producers in the coniferous woodland include conifers - which produce cones with seeds rather than flowers - shrubs and grasses. One simplified food chain is grass eaten by deer, the deer eaten by a mountain lion and the mountain lion's body decomposed by bacteria and fungi. Another food chain consists of pine
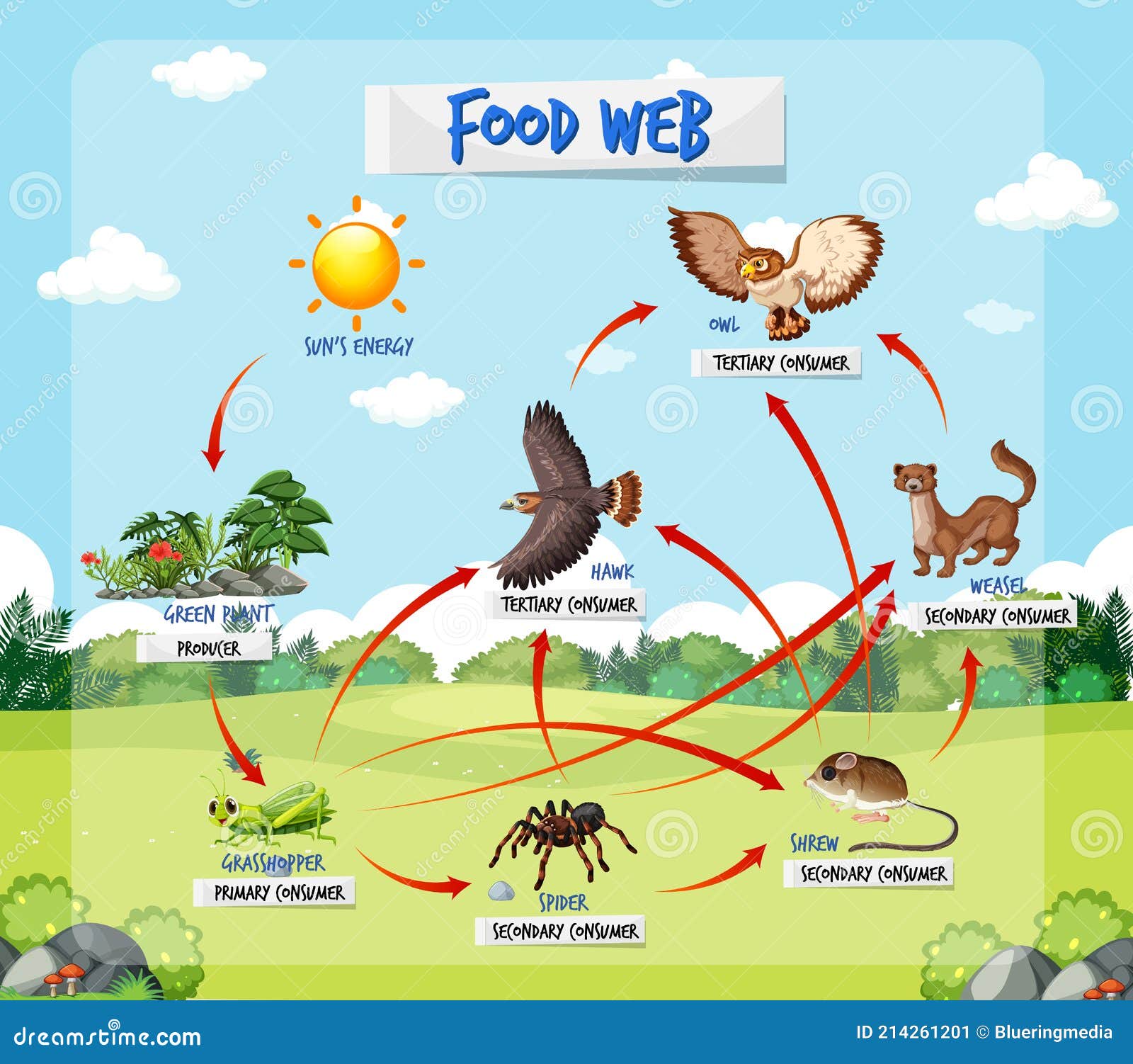
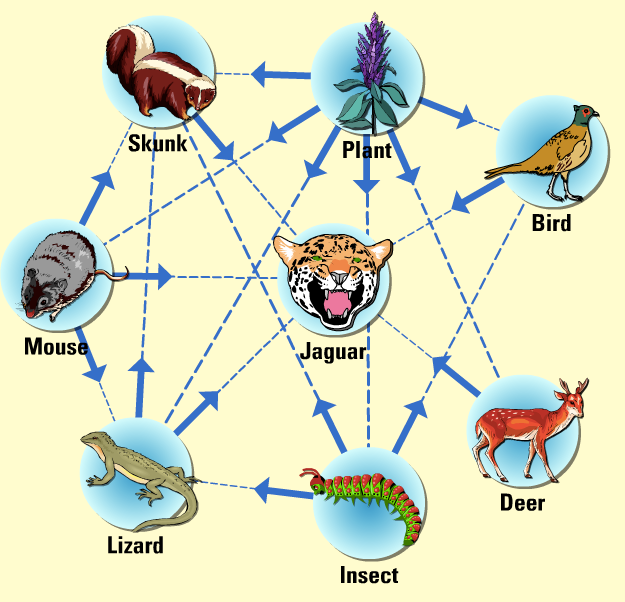
Food Web Biology Diagrams
The adaptation of specialized teeth for crunching through exoskeletons underscores their evolutionary niche in the food chain. C. Fruits and Vegetation. Inclusion of Fruits, Vegetables, and Plant Matter Ecologically, woodpeckers' diets resonate in forest ecosystems, exerting influence on insect populations and tree health. Opossums, with Woodpecker Diet and Food Sources. Woodpeckers as wild birds can easily find abundant food sources in the wild. However, the exact foods for woodpeckers vary, depending on their species. The most common foods include suet, insects, peanuts, peanut butter, black oil sunflower seeds, nectar, sap, acorn, etc. 1. Insects

The hairy woodpecker is a medium-sized woodpecker found across much of North America. Like other woodpeckers, it plays an important role in the ecosystem by creating cavities in trees for nesting and roosting sites. The hairy woodpecker's diet consists mainly of insects, especially the larvae of wood-boring beetles. Woodpeckers are essential to the animal food chain as prey and predators. In their role as prey, they provide food to many organisms, thus promoting survival. As predators, woodpeckers help regulate the local population of the different kinds of insects they feed on. In essence, they promote the existence of a balance in their ecosystem. Several North American woodpeckers, including the Acorn Woodpecker, Red-headed Woodpecker, and Red-bellied Woodpecker, exhibit food caching behavior, storing food items for later consumption. Acorns are the most common cached item, but other nuts and insects are also stored. Role of the woodpeckers foraging techniques in forest ecosystems
