Mitochondrial structure and function Quiz Biology Diagrams Popularly known as the "Powerhouse of the cell," mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) are a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms.They are found inside the cytoplasm and essentially function as the cell's "digestive system." They play a major role in breaking down nutrients and generating energy-rich molecules for the cell. 9. Can mitochondrial function be improved? Lifestyle factors such as exercise, diet, and certain supplements might improve mitochondrial function, but research in this area is ongoing. 10. Are mitochondria involved in aging? Some research suggests that changes in mitochondrial function are linked to the aging process. The final reaction in the mitochondrial function chain is one in which oxygen from cellular respiration undergoes reduction to form water. The end products of the reactions are water and ATP. Cell structure with membrane-bound organelles has played an important part in human evolution and mitochondria have made an essential contribution

Learn how mitochondria function in cell death and regeneration. Mitochondria are parts of a human cell known as the "energy factories." Most human cells, animal cells, and plant cells contain hundreds or even thousands of mitochondria. Lumbar Spine Anatomy and Function. Labeled Anatomy of the Skeletal System. Voluntary Muscles vs The ability to reshape cristae allows mitochondria to fine-tune their function, ensuring that energy production aligns with cellular needs. Furthermore, cristae play a role beyond energy metabolism. Their unique architecture creates microdomains that compartmentalize various mitochondrial functions, including the regulation of apoptosis.
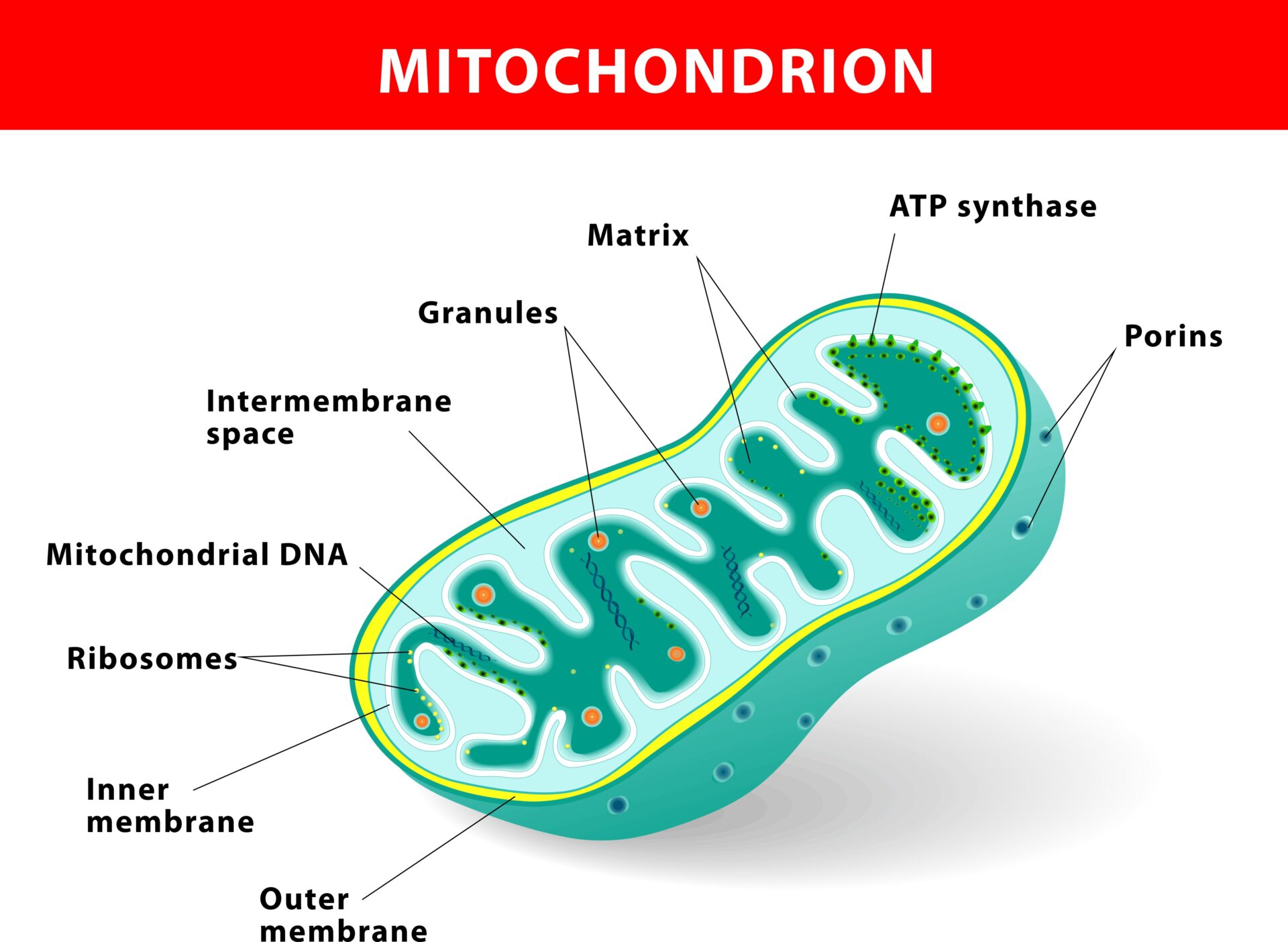
Mitochondrial Function and Health in Eukaryotic Cells Biology Diagrams
Function of Mitochondria. Mitochondria produce ATP through process of cellular respiration—specifically, aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen. The citric acid cycle, or Krebs cycle, takes place in the mitochondria. This cycle involves the oxidation of pyruvate, which comes from glucose, to form the molecule acetyl-CoA. Mitochondrion, organelle found in most eukaryotic cells, the primary function of which is to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate. Mitochondria also store calcium for cell signaling activities, generate heat, and mediate cell growth and death. They typically are round to oval in shape. The two main functions of mitochondria are: 1) promoting the growth of new cells and in cell multiplication, and 2) serving as the 'energy currency' of the cell by synthesizing high-energy phosphate molecule - ATP Other Important Functions:. Producing body heat by the accumulation of brown-fat; Controlling various cellular activities such as cell differentiation, cell signaling, cell
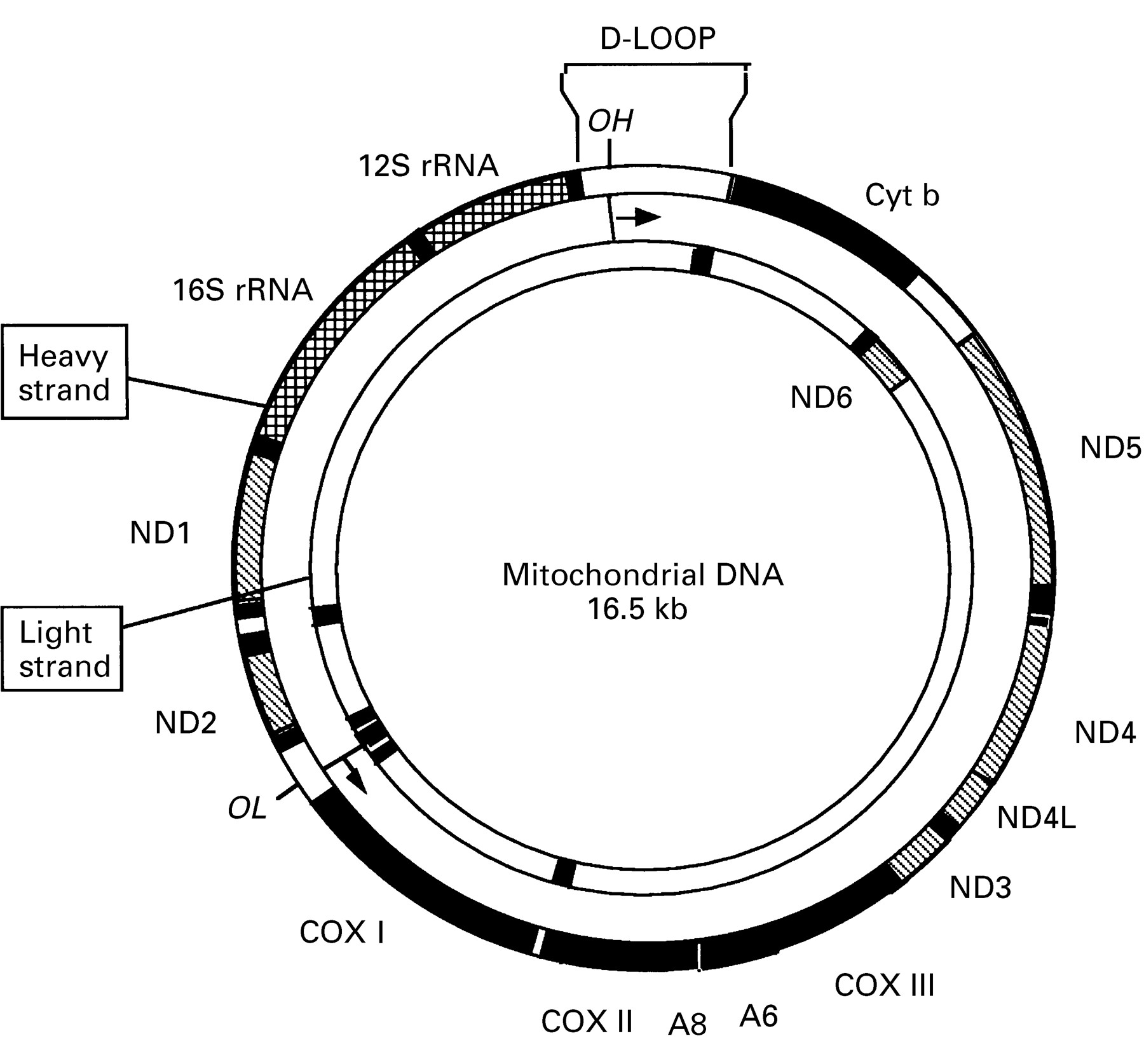
Estrogenic control of mitochondrial function and biogenesis. Characterization of the human heart mitochondrial proteome. What to know about nail anatomy. Medically reviewed by Cynthia Cobb
