Muscle Spindle Muscle Stretch Reflex Biology Diagrams For this reason the stretch reflex is known as a spinal cord reflex and is completely involuntary. If the reflex was mediated by the brain precious time could be lost before the protective impulse to contract reached a stretched muscle, resulting in….a potentially far more serious injury. Muscle spindles are active with all exercise. This process is called the stretch reflex. When a muscle spindle's associated muscle is rapidly stretched, the spindle can cause two things to happen: (1) it may signal its muscle to contract to prevent it from going too far, too quickly in the stretch; and (2) it can inhibit the opposing muscle (the antagonist to the muscle being stretched

Muscle spindles are stretch receptors within the body of a skeletal muscle that primarily detect changes in the length of the muscle. After stroke or spinal cord injury in humans, spastic hypertonia (spastic paralysis) often develops, whereby the stretch reflex in flexor muscles of the arms and extensor muscles of the legs is overly The monosynaptic stretch reflex, sometimes called the muscle stretch reflex or deep tendon reflex, is a reflex arc that facilitates direct communication between sensory and motor neurons innervating the muscle. This reflex initiates inside the muscle spindle, which detects both the magnitude and rate of muscle stretch. When the muscle is subjected to a stretch stimulus, sensory impulses are Muscle spindles are small sensory organs with an elongated shape, involved in proprioception. Image 2: Mammalian muscle spindle showing typical position in a muscle (left), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle) and expanded schematic (right). The spindle is a stretch receptor with its own motor supply consisting of several intrafusal muscle fibres.

Muscle Spindles Biology Diagrams
This monosynaptic reflex arc is variously referred to as the "stretch," "deep tendon," or "myotatic reflex," and it is the basis of the knee, ankle, jaw, biceps, or triceps responses tested in a routine neurological examination. The tap of the reflex hammer on the tendon stretches the muscle and therefore excites a volley of activity from the muscle spindles in the afferent axons. The stretch reflex is the contraction of a muscle that occurs in response to its stretch. It is not controlled by higher functioning centre i.e. the brain, and is a monosynaptic response that is transmitted to the spinal cord.Our body needs to be able to respond without our cortical input. In this article we will discuss the stretch reflex, the anatomy that underpins it, as well as the The pathway starts when the muscle spindle is stretched (caused by the tap stimulus in the knee jerk reflex). The muscle spindles are responsible for detecting the length of the muscles fibres. When a stretch is detected it causes action potentials to be fired by Ia afferent fibres. These then synapse within the spinal cord with α-motoneurones
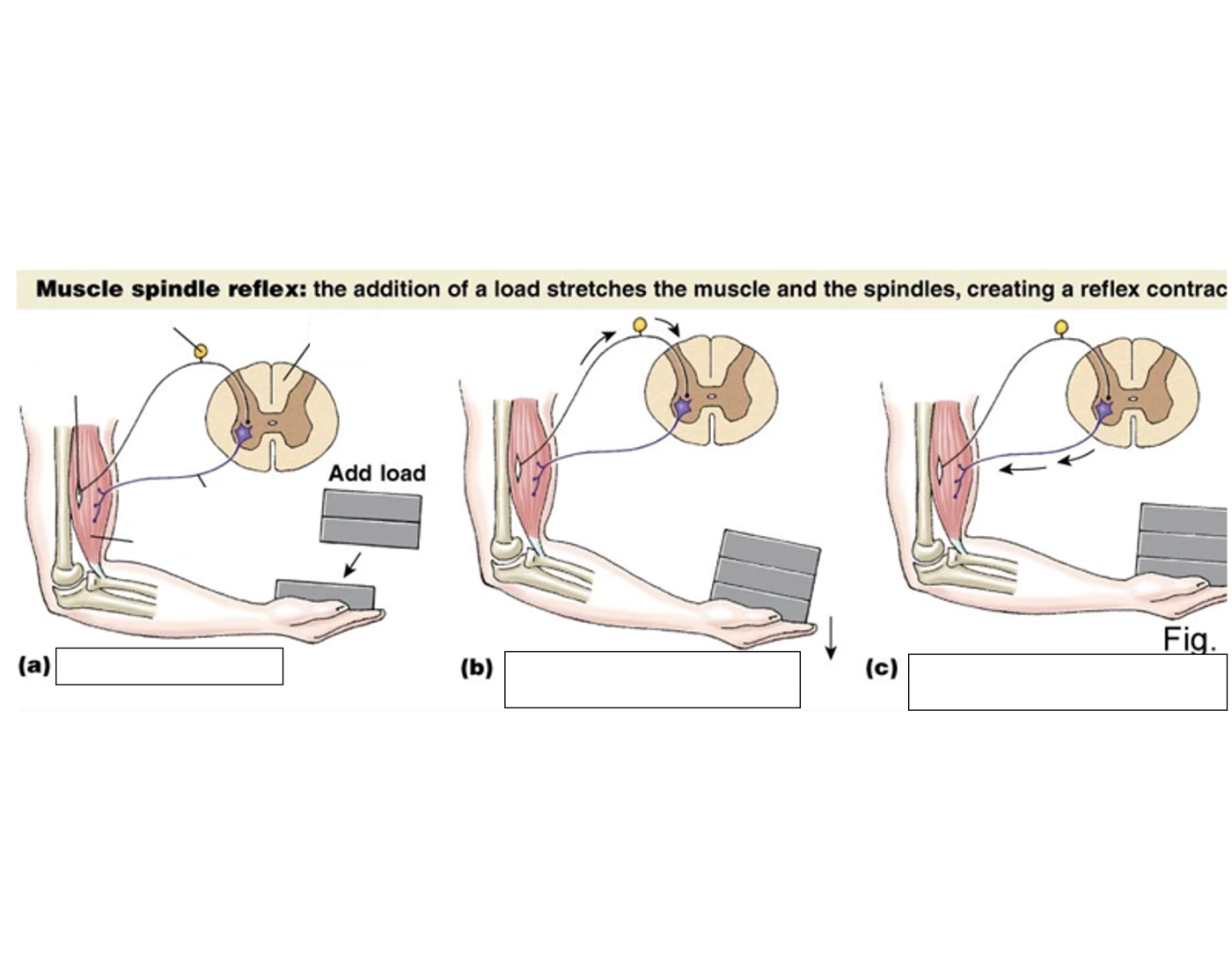
The stretch reflex is designed as a protective mechanism, to prevent strain and tear injuries to the muscles and tendons. When the muscle spindle is excited an impulse is immediately received to contract the muscle, thereby protecting it from being pulled forcefully or stretched beyond a normal range of motion. The stretch reflex is accomplished through several different structures. In the muscle, there are muscle spindles, whose intrafusal muscle fibers lie parallel to the muscle and sense changes in length and velocity. The afferent sensory neuron is the structure that carries the signal from the muscle to the spinal cord.
