Physiological Effects of Chronic Hypoxia Biology Diagrams Mechanisms of cell cycle control in response to hypoxia Cells placed in severe hypoxia undergo a rapid cessation of cell cycle progression and DNA synthesis. The arrest is complex, and has components in multiple phases of the cell cycle, with G1/S, S phase and G2/M arrests all being reported in the literature [87] . The cell cycle is an important cellular process whereby the cell attempts to replicate its genome in an error-free manner. As such, mechanisms must exist for the cell cycle to respond to stress signals such as those elicited by hypoxia or reduced oxygen availability. This review focuses on the role …

Cartoon representation of the signaling pathways causing cell cycle arrest at different points in the cell cycle (red circles) in response to hypoxia and reoxygenation.(1) Moderate hypoxia arrests cells at the restriction point (START) of the G1-phase in a HIF-dependent manner. pRB indicates the phosphorylated Retinoblastoma protein.(2) Severe hypoxia or anoxic conditions additionally cause an

Role of Hypoxia in the Control of the Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
The hypoxia response mounted by the HIFs promotes cell survival and energy conservation. As such, this response has to deal with important cellular process such as cell division. In this review, the integration of oxygen sensing with the cell cycle will be discussed.

The transcriptional response to hypoxia and the role of hypoxia inducible factors have been extensively studied. Yet, hypoxic cells also adapt to hypoxia by modulating protein synthesis

Role of Hypoxia in the Control of the Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
HIFs bind to hypoxia response elements (HREs) in the promoter regions of a large number of targets, including those involved in cell survival, angiogenesis, glycolysis, and invasion/metastasis. Certain mutations in TSC2 confer a growth advantage to cells by repressing hypoxic mTORC1 inhibition and hypoxia-induced cell cycle arrest 135.
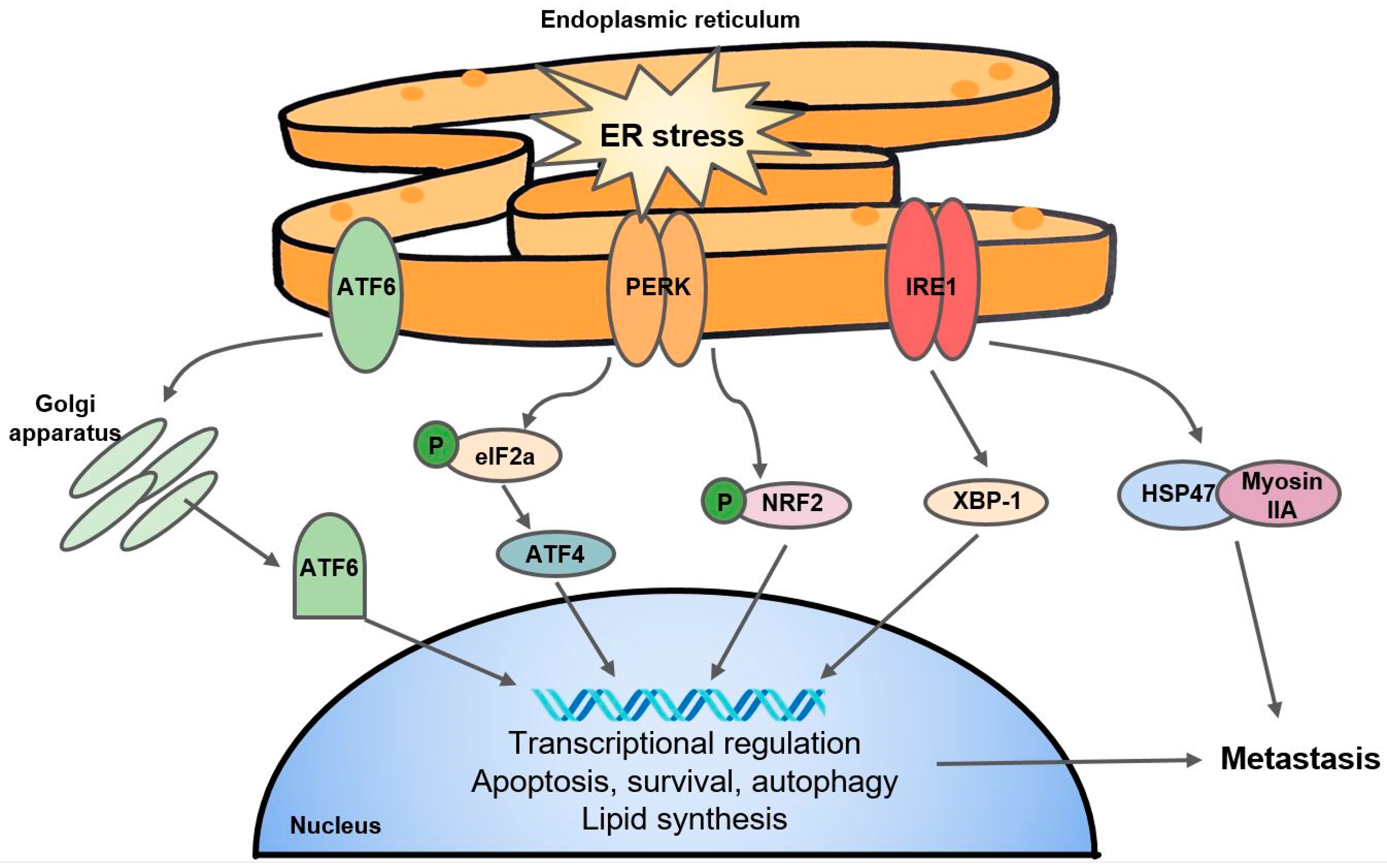
The expression of genes regulating the response to hypoxia—Hif1a, Epas1, Hif3a, and Vegf—inflammation—Nfkb, Il1b, Il6, Tnfa, Il10, and Tgfb—and the cell cycle and apoptosis—Trp53, Pten, Cmet, Egf, Egfr, Pcna, Mki67, and Bax, Bcl2—as well as genes encoding the epithelial barrier components—Muc1, Muc13, Cldn2, and Cldn7—in the Cyclin D1, a downstream target of p38 , has been implicated in regulating progression through the G 1 phase of the cell cycle (45, 46). In PC12 cells, hypoxia causes a decrease in cyclin D1 protein levels and also causes cells to accumulate at the boundary between the G 0 and G 1 phases of the cell cycle . Both of these effects are partially The cell cycle is an important cellular process whereby the cell attempts to replicate its genome in an error-free manner. As such, mechanisms must exist for the cell cycle to respond to stress signals such as those elicited by hypoxia or reduced oxygen availability. This review focuses on the role of transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms initiated in hypoxia that interface with
