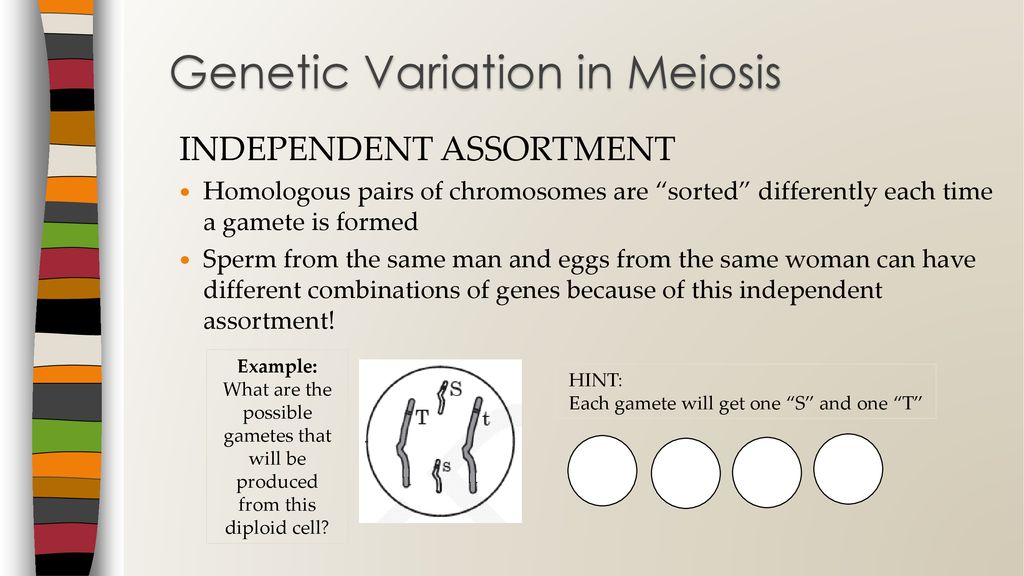
ppt download Biology Diagrams Meiosis: Sources of Genetic Variation. Having genetically different offspring can be advantageous for natural selction. Meiosis has several mechanisms that increase the genetic diversity of gametes produced. Both crossing over and independent assortment (random orientation) result in different combinations of alleles in gametes. Crossing over. Crossing over is the process by which non-sister Genetic variation is increased by meiosis. During fertilisation, 1 gamete from each parent combines to form a zygote. Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis, each gamete contains a different set of DNA. This produces a unique combination of genes in the resulting zygote. Meiosis is the process of producing gametes, which are sperm cells and egg cells. Gametes have only half the number of chromosomes that normal cells have, because a sperm and an egg fuse to form a cell that has the full number of chromosomes. Genetic diversity arises due to the shuffling of chromosomes during meiosis.
+ways..jpg)
Meiosis is a crucial biological process that ensures genetic diversity among organisms. It plays a vital role in the reproduction of sexually reproducing species by introducing variation into the gene pool, which is essential for evolution and adaptation. Introduction: Meiosis Creates Genetic Variation. One key idea to take away from everything that we've learned about meiosis so far is that meiosis reduces chromosome number from diploid to haploid.. Here's a second idea: meiosis, along with fertilization, creates genetic variation.That second idea is going to be the focus of this tutorial. Meiosis is important for producing variation because it shuffles the genetic material in a way that leads to the formation of new combinations of alleles, or different versions of genes. This variation contributes to the diversity of traits found in a population and is an important mechanism for the evolution of species.

Meiosis: Sources of Genetic Variation Biology Diagrams
Genomic diversity and genetic variation is produced through the process of meiosis due to chromosomal recombination and independent assortment. Each daughter cell created is genetically half-identical to that of its parent cell yet distinctly different from its parent cell and other daughter cells. Meiosis and fertilization create genetic variation by making new combinations of gene variants (alleles). In some cases, these new combinations may make an organism more or less fit (able to survive and reproduce), thus providing the raw material for natural selection.

Meiosis: Introduces genetic variation, which is a driving force for evolution. Mitosis: Does not introduce genetic variation in the same way; its primary role is in growth and repair. Locations in Organisms: Meiosis: Occurs in the germ cells of the gonads (ovaries and testes in animals).