res stock photography and images Biology Diagrams What are Phytoplankton? Phytoplankton are mostly microscopic, single-celled photosynthetic organisms that live suspended in water. Like land plants, they take up carbon dioxide, make carbohydrates using light energy, and release oxygen. They are what is known as primary producers of the ocean—the organisms that form the base of the food chain.
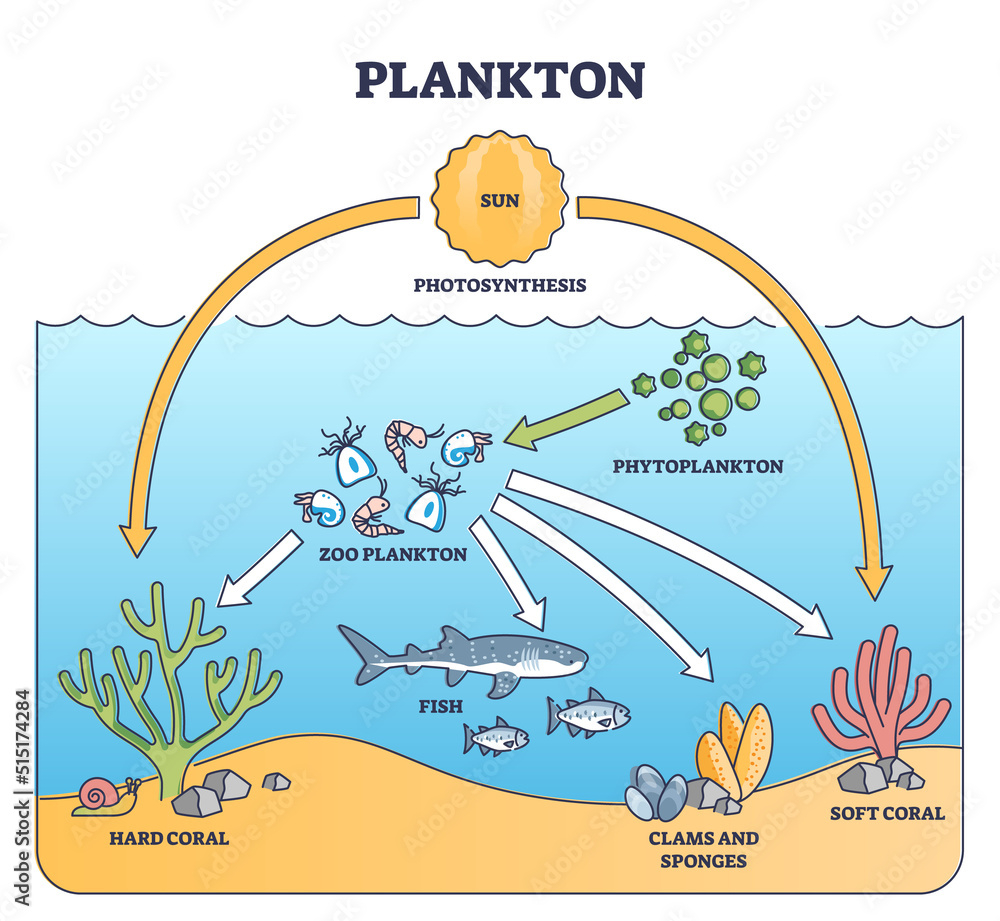
Food webs describe who eats whom in an ecological community.Made of interconnected food chains, food webs help us understand how changes to ecosystems — say, removing a top predator or adding nutrients — affect many different species, both directly and indirectly.. Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs. They are eaten by primary consumers like zooplankton, small fish Some of this food passes directly along the food chain when zooplankton eat the phytoplankton and in turn are consumed by larger animals such as fish, whales, squid, shellfish and birds. Food produced by phytoplankton can also enter another pathway dominated by bacteria (and possibly viruses). Humans rely heavily on marine resources for food, livelihoods, and recreation. Plankton, being the cornerstone of the marine food chain, indirectly support millions of people globally. A healthy plankton population ensures the sustainability of fish stocks and other marine resources that human populations depend on. Plankton Research and Monitoring
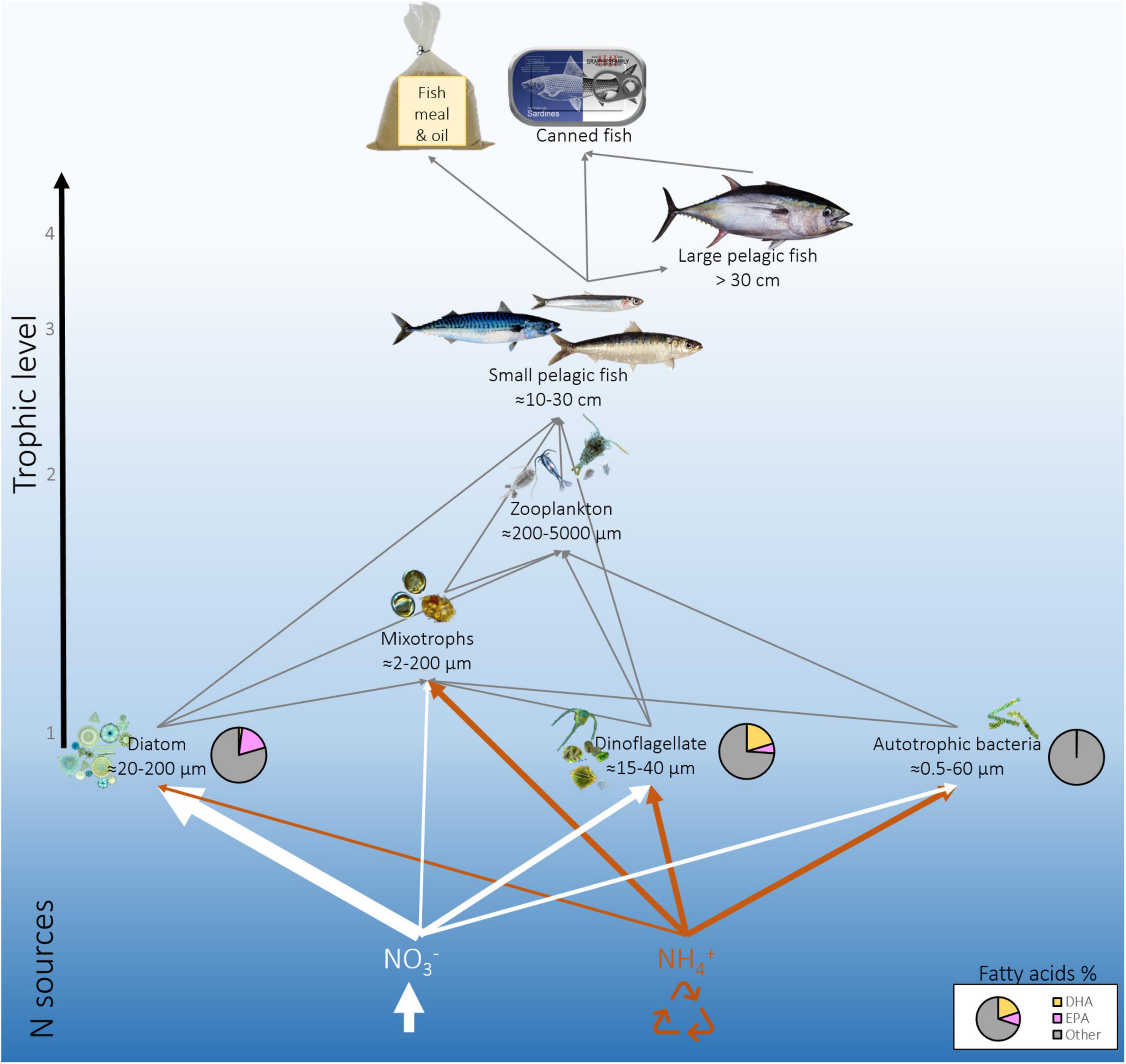
WHOI - Woods Hole Oceanographic ... Biology Diagrams
Most of these aquatic species are tied together through the food web. Level One: Photo autotrophs The foundation of the sea's food chain is largely invisible. Countless billions of one-celled organisms, called phytoplankton, saturate sunlit upper-ocean waters worldwide.

Phytoplankton are similar to plants and use sunlight and nutrients to grow. They are the base of several aquatic food webs and provide food for many sea creatures, but can also cause harmful algal blooms. Ocean ecosystem food chains are perhaps the most primitive and curious levels of food webs. With oceans covering over 70 % of the Earth's surface, owing to that large expanse, they are home to over 230,000 documented marine species. The chain starts with primary producers, such as Phytoplankton, and moves up to apex predators like sharks and orcas.
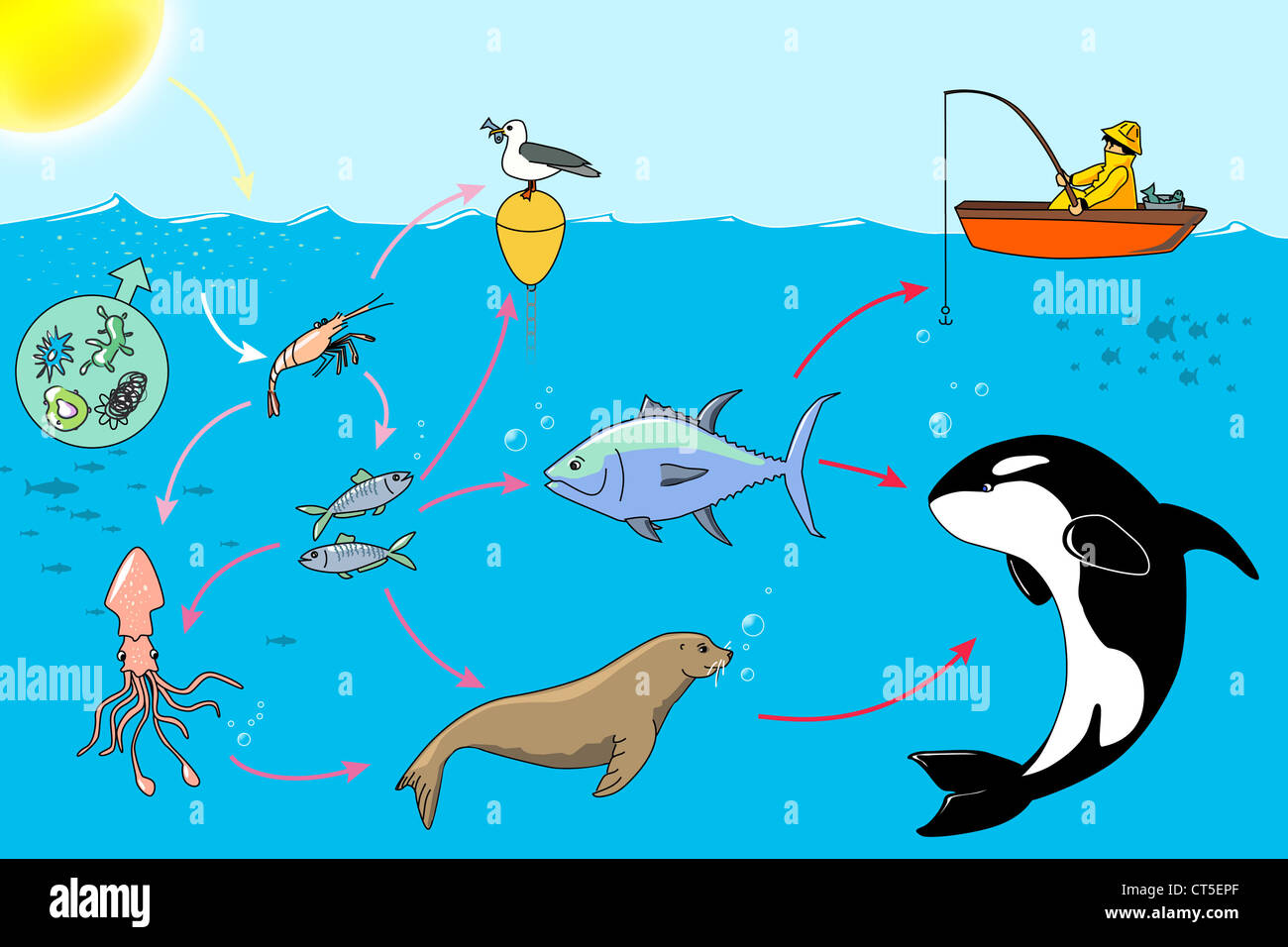
Marine food web Biology Diagrams
Feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains - in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term 'food web' more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers They form the 2nd level of the trophic pyramid and consume phytoplankton. Zooplankton are eaten by the 1st level
