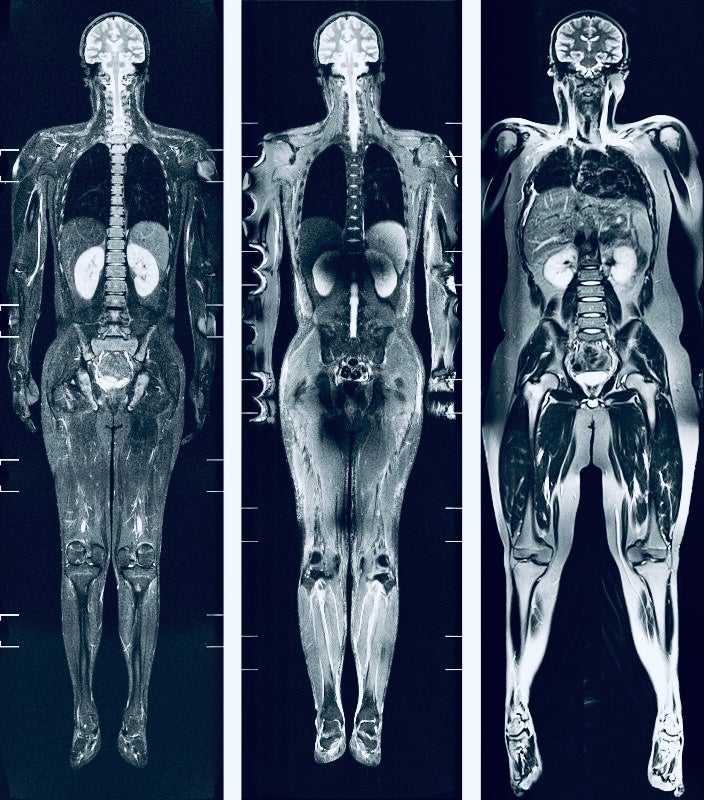
Resonancia magntica de columna cervical Biology Diagrams It provides unparalleled detail of soft tissues, the brain, and the spinal cord and offers insights into both structural and functional aspects of the body. Understanding MRI Anatomy. Before interpreting any abnormalities on an MRI scan, it is essential to be familiar with normal anatomy as seen in different sequences. Brain MRI Anatomy Here are some of the potential conditions that may be detected through a Whole Body MRI scan: Cancers: Whole Body MRI scans may help early detect certain types of cancers. For instance, the scan evaluates the head and neck for any detectable cancers. The chest is also assessed for masses greater than 1.5 cm, potentially indicating lung cancer

The slide presentation demonstrates an approach to body MRI for common indications in the abdomen and pelvis, incorporating clinical information, knowledge of imaging patterns, and various scoring Interpreting a MRI Scan Image View. MRI scans, much like computed tomography, typically produce three anatomical views; sagittal, coronal and axial (similar to the planes of the body). When interpreting axial views, it is important to appreciate that the image is viewed from the feet upwards - and so the left-hand side of the image refers to Patients undergoing routine health checkups who want a more in-depth scan for peace of mind. Full Body MRI Cost Analysis. Comprehensive full body MRI packages without add ons, range between $650 and $1500. Premium services, which may include additional modalities such as CT scan, ultrasound, lab work, etc, range between $3995 to $5995.

Body MRI Approach: Guide for Common Indications Biology Diagrams
The cost of an MRI scan in Dubai varies depending on factors such as the type of scan, including brain, full-body, or specific body part imaging; the quality and reputation of the medical facility; the geographic location of the service; and whether contrast agents are required to enhance image clarity. CT scans use X-rays (with harmful radiation) to create cross-sectional images of the body, while MRI utilizes powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images without the use of harmful radiation. Since MRIs do not use harmful radiation, they are much more suitable for whole body screening as you could perform scans as frequently as needed without increasing the risk of radiation
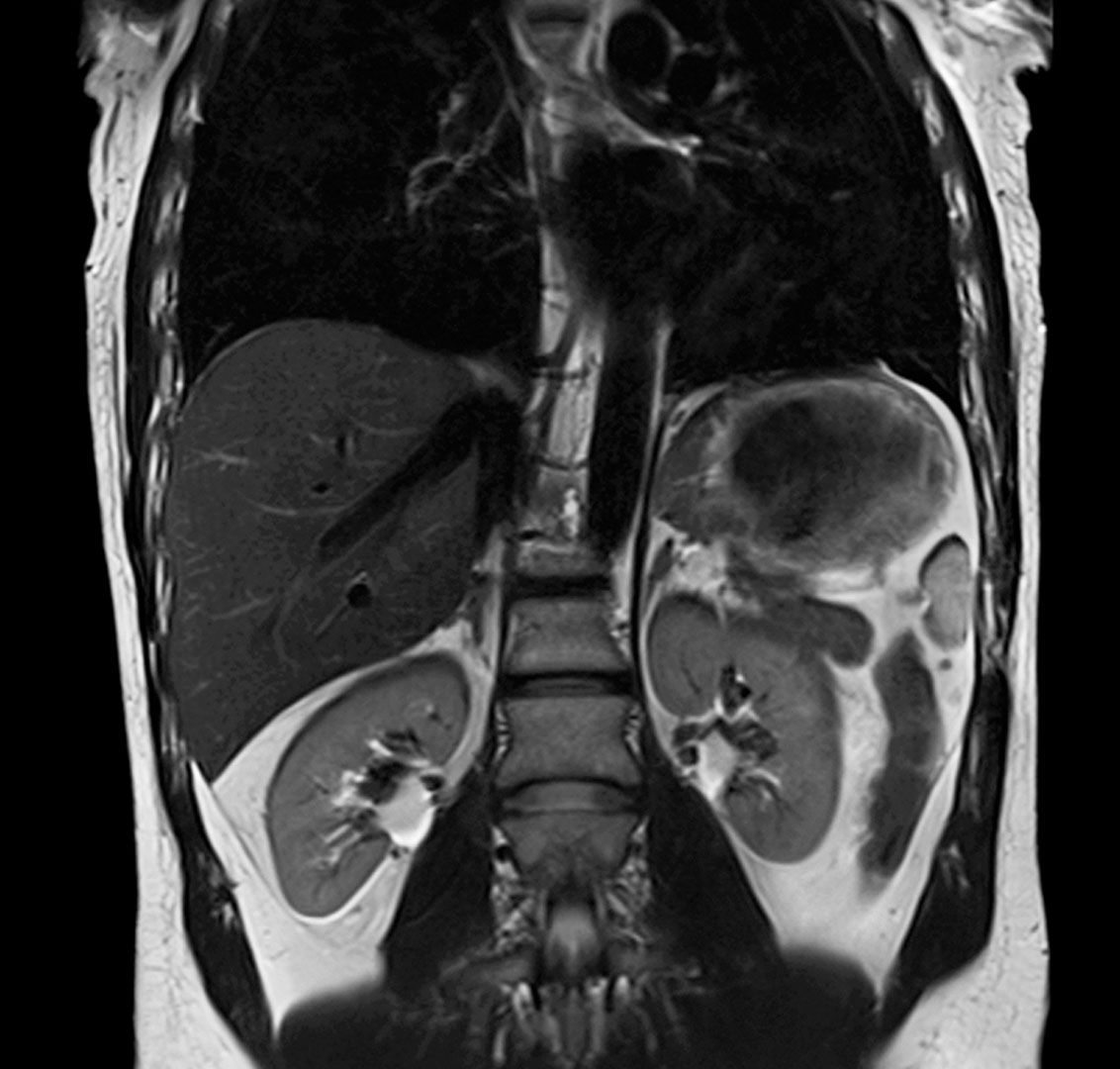
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners allow physicians to perform a whole-body scan (also known as a full-body scan), without ionizing radiation from Computed Tomography (CT) scans. A whole-body MRI scan looks at the body from head to toe in order to find cancers, inflammation or obstructive processes in the body. In the head, the exam can Abstract. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) is an imaging method without ionising radiation that can provide WB coverage with a core protocol of essential imaging contrasts in less than 40 minutes, and it can be complemented with sequences to evaluate specific body regions as needed. Type of Book: A pocket atlas of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of anatomic areas of the body. Scope of Book: A general overview of body anatomy on MRI is presented. Contents: This atlas covers anatomy of the chest, abdomen, pelvis, thigh, knee, calf, foot and ankle, shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, and wrist and hand.