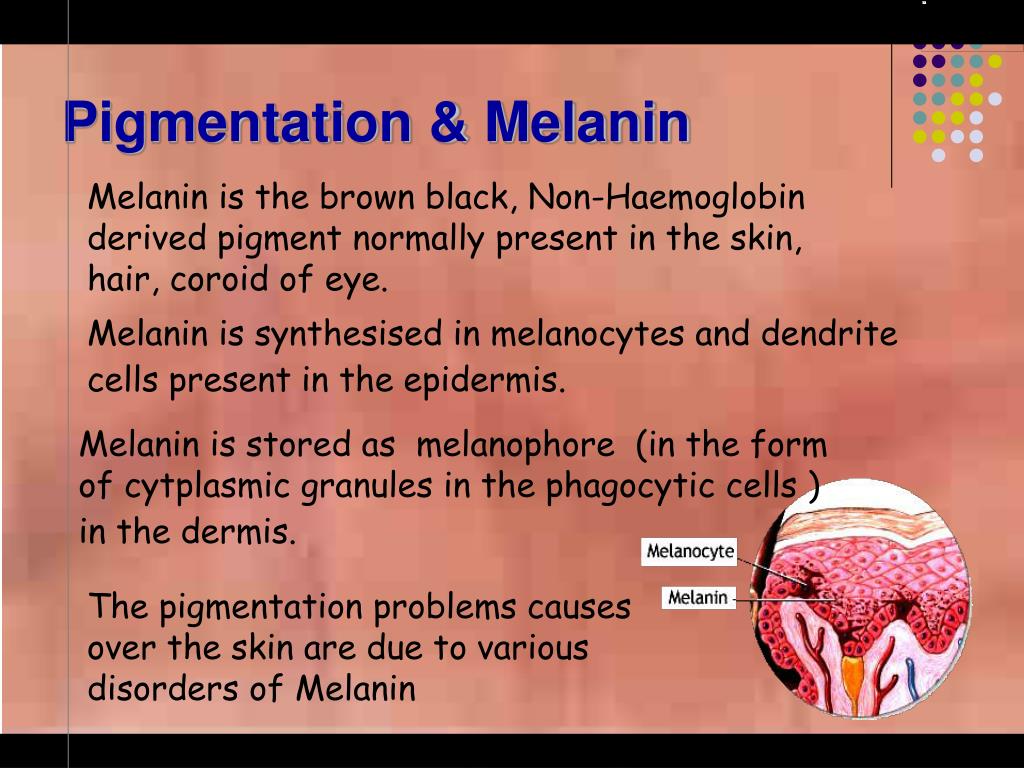
Skin Pigment Melanin Biology Diagrams Pigmentation of the skin results from the accumulation of melanin-containing melanosomes in the basal layer of the epidermis. Differences in skin pigmentation result both from the relative ratio of eumelanin (brown-black) to pheomelanin (yellow-red), as well as the number of melanosomes within melanocytes. Pheomelanin accounts for the Skin pigmentation refers to the color of your skin. It's determined by the amount and type of melanin, a pigment made by specialized skin cells known as melanocytes. Changes in melanin production can cause pigment disorders, such as hyperpigmentation (dark spots), hypopigmentation (light spots), depigmentation (white spots or patches).

The actual skin color of different humans is affected by many substances, although the single most important substance is the pigment melanin. Melanin is produced within the skin in cells called melanocytes and it is the main determinant of the skin color of darker-skin humans. The pigment melanin gives skin its color. It is made by specialized skin cells called melanocytes. When melanocytes become damaged, skin color can be affected. It can affect one small area of the body or the entire body, depending on the cause and progression of the disorder. Keywords: skin pigmentation, melanin, tyrosinase inhibitors, hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, vitiligo, skin lightening, depigmentation. 1. Introduction. Skin pigmentation, which refers to how much melanin the body generates, determines the color of the skin. The two main types of melanin, eumelanin, and pheomelanin, are produced by
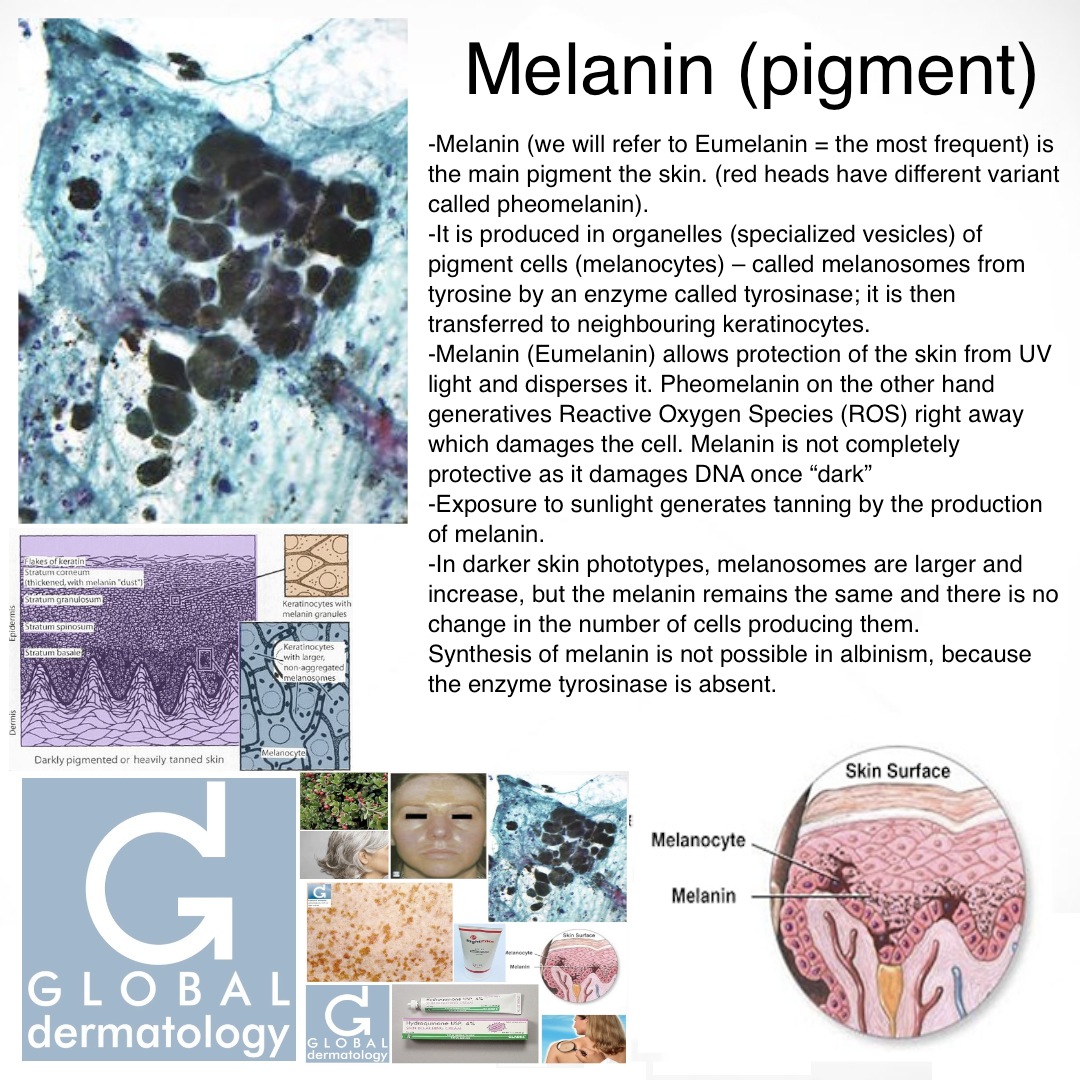
Melanin: Definition, function, benefits, and more Biology Diagrams
Melanin is responsible for the pigmentation of the skin and hair. It also protects the skin from the sun. Albinism is a genetic condition that causes people to have very little or no melanin Pigmentation disorders can cause hyperpigmentation (increased skin color) and hypopigmentation (reduced skin color). These changes can be localized (in certain areas) or generalized (all over). Conditions affected by melanin include: Albinism: This inherited disorder reduces melanin pigment in skin, hair, and eyes.It causes white hair, pale skin, and pink or blue eyes.

Melanin is a natural substance that determines the color of hair, skin, and eyes in people and animals. Special cells called melanocytes make melanin. Special cells called melanocytes make melanin. Melanin is a pigment responsible for skin tone. Melatonin is a hormone that regulates your waking and sleeping cycle. Does melanin cause vitamin D deficiency? Some experts believe that people who have darker skin are more prone to vitamin D deficiency than people with lighter skin. This is because excess melanin absorbs the UV rays responsible