The 3 Anatomical Body Planes and The Movements In Each Biology Diagrams The coronal plane, the sagittal plane, and the parasaggital planes are examples of longitudinal planes. Anatomical Planes in a Human: There are three basic planes in zoological anatomy: sagittal, coronal, and transverse. A human in the anatomical position, can be described using a coordinate system with the Z-axis going from front to back, the A "parasagittal" plane is any sagittal plane that does not run perfectly down the midline of the body. Oblique Planes. An oblique plane is a plane that can literally be any type of angle other than a horizontal or vertical angle. In fact, the word "oblique" means that something is not parallel or a right angle. Introduction. Anatomical planes are imaginary planes/2D surfaces used to divide the body to facilitate descriptions of location and movement.. The anatomical position is used as a reference when describing locations of structures and movements.It is an upright position with arms by the side and palms facing forward. Feet are parallel with toes facing forward.

The Interactive Sagittal Section is meant to be illustrative, not normative. For example, the alveolar fricatives /s/ and /z/ are shown here as apico-alveolar, but they can also be made with a lamino-alveolar constriction. The general structure of this sagittal section is based on diagrams in The sounds of language: An introduction to

Anatomy and Physiology: Anatomical Planes and Cavities Biology Diagrams
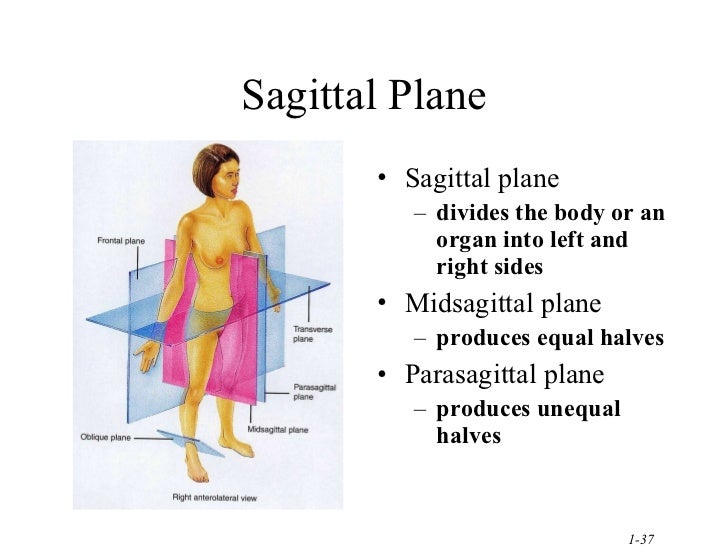
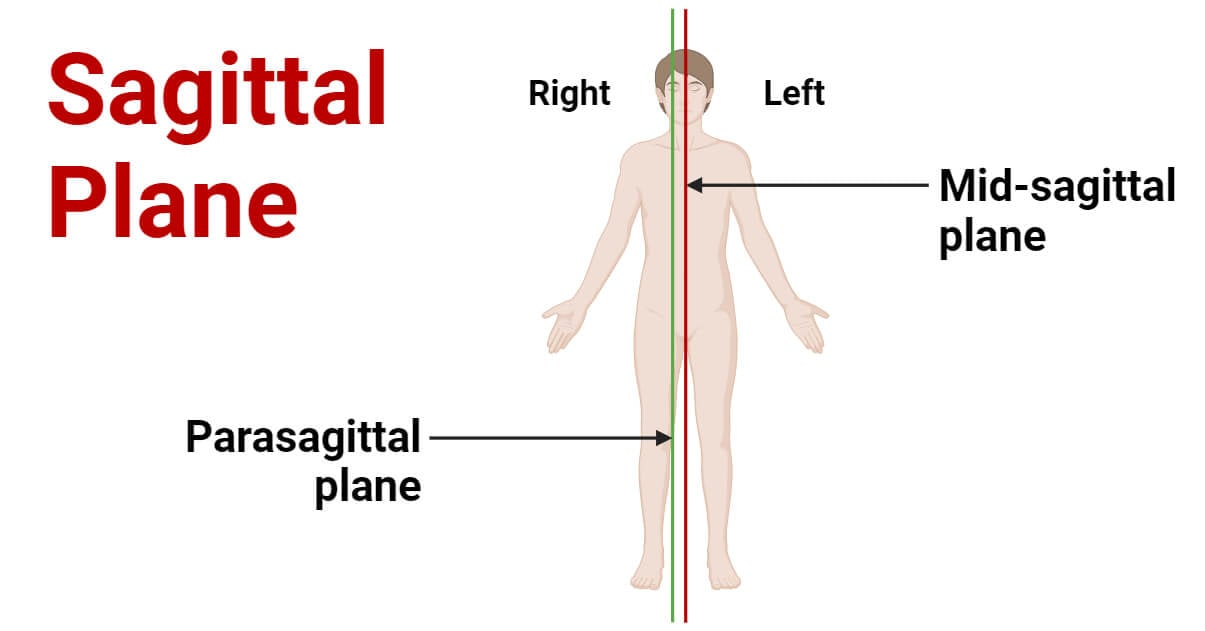
Three basic reference planes are used in anatomy A sagittal plane, also known as the longitudinal plane, is perpendicular to the ground and divides the body into left and right. The midsagittal or median plane is in the midline i.e. it would pass through the midline structures (e.g. navel or spine), and all other sagittal planes (also referred to as parasagittal planes) are parallel to it.
The anatomical planes are hypothetical planes used to describe the location of structures in human anatomy. They are applied to the human body in the anatomical position. In this article, we shall look at the anatomical planes in more detail - in particular, the three most commonly used planes: sagittal, coronal and transverse.
Anatomical Position: Body Planes and Sections Biology Diagrams
The three planes of motion include coronal (frontal), sagittal (longitudinal), and transverse (axial) planes. These planes involve moving side-to-side, front and back, or rotationally, respectively. The sagittal plane (/ ˈ s æ dʒ ɪ t əl /; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. [1] It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divide it into two equal parts (mid-sagittal), or away from the midline and divide it into unequal parts (para-sagittal). The art kind, or in more technical terms the area of a two-dimensional surface. When used in conjunction with anatomy, planes are used to divide the body and its parts, which allows you to describe the views from which you study the body. that a good number of the pictures and diagrams make use of planes. Here is a list of commonly used
