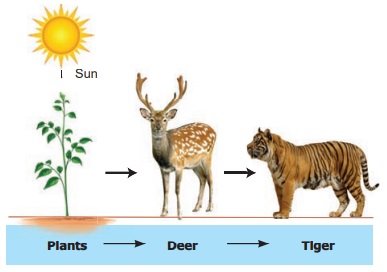
Tiger Food Chain Diagram Biology Diagrams The grass, deer and tiger form a food chain (Figure 8.2). In this food chain, energy flows from the grass (producer) to the deer (primary consumer) to the tiger (secondary consumer). A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks (Figure 8.3). The tiger's food chain is not just about survival; it's about the intricate balance of ecosystems across numerous habitats. As apex predators, tigers are essential to maintaining that balance, influencing their environment significantly. By understanding their food chain and the factors that impact it, we can take proactive steps toward Food Chain Examples With Diagram. April 23, 2024 April 19, 2024 by Amit Sabhadiya. grass → grasshopper → frog → snake → eagle, and the food chain: grass → deer → tiger. All of the interconnected and overlapping food chains in a habitat make up a food web.

Typically, a food chain is represented by a diagram where arrows show the direction of energy and nutrients flow. Many herbivores eat grass, and deer can eat other plants besides grass. Even a tiger can eat many types of animals and plants. Thus, each animal is part of multiple food chains. All interconnected to make a food web.
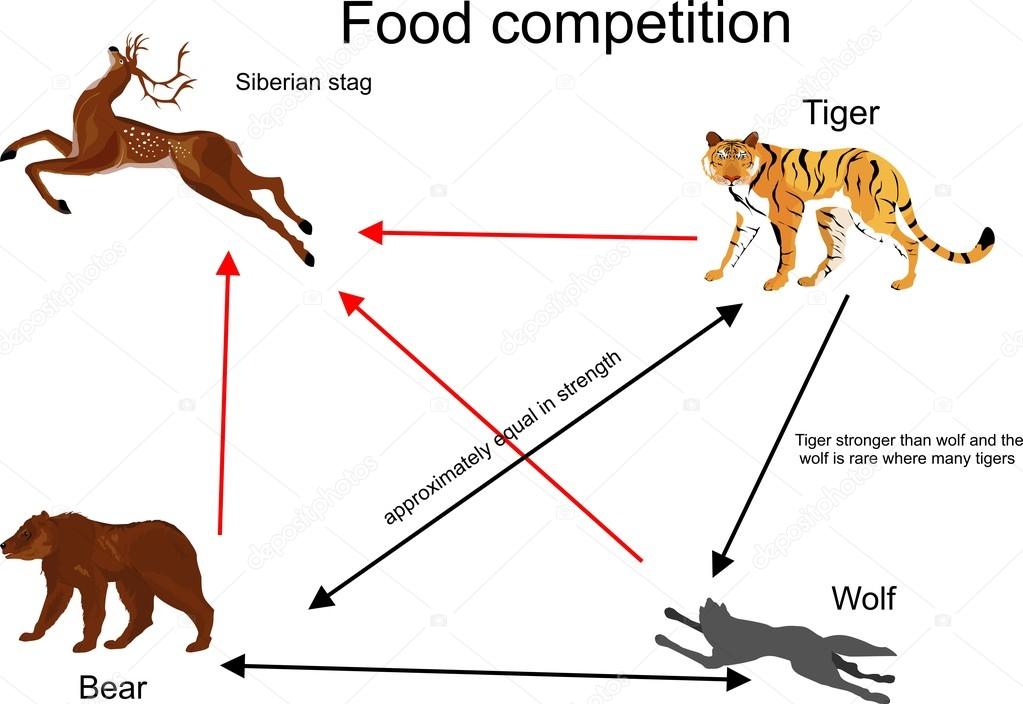
hunting, prey and captive feeding. Biology Diagrams
Learn how tigers are apex predators and their role in the food chain. Explore the relationship between tigers and their prey, decomposers, and other predators, and the threats to their conservation. A diagram of the food chain: The tiger is at the top of the food chain; their only direct threat is man. Predators like the tiger thin out hoof stock and prevent their populations growing to the point where vegetation would be over-used; this would lead to a break down of the land.
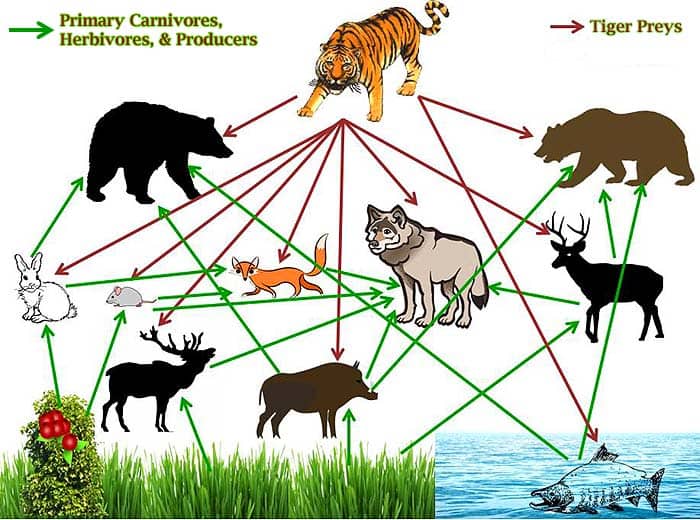
Explore the tiger food chain and tiger food web. Discover the primary, secondary, and tertiary animals, as well as predators and other threats to the tiger species. Updated: 11/21/2023 Tiger Food Chain Diagram. The above diagram shows that the tiger sits at the top of the food chain in the ecosystem with no predators and feeds on the primary carnivores and herbivores directly. The second layer represents the primary carnivores, such as foxes and wolves, which feed on the herbivores.